BiaŇāystok University on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
BiaŇāystok is the largest city in northeastern
 In 1661 it was given to
In 1661 it was given to  The end of the eighteenth century saw the
The end of the eighteenth century saw the  .
The first anarchist groups to attract a significant following of Russian workers or peasants were the
.
The first anarchist groups to attract a significant following of Russian workers or peasants were the  During
During  With the beginning of
With the beginning of
 BiaŇāystok is situated in the BiaŇāystok Uplands ( pl, Wysoczyzna BiaŇāostocka) of the Podlaskie Plain ( pl, Nizina P√≥Ňānocnopodlaska), part of what is known collectively as the ''Green Lungs of Poland''. It is situated by road northeast of
BiaŇāystok is situated in the BiaŇāystok Uplands ( pl, Wysoczyzna BiaŇāostocka) of the Podlaskie Plain ( pl, Nizina P√≥Ňānocnopodlaska), part of what is known collectively as the ''Green Lungs of Poland''. It is situated by road northeast of
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
BiaŇāystok is located in the BiaŇāystok Uplands of the Podlachian Plain on the banks of the BiaŇāa River, by road northeast of Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
. It has historically attracted migrants from elsewhere in Poland and beyond, particularly from Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
. This is facilitated by the nearby border with Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, –†–Ķ—Ā–Ņ—É–Ī–Ľ–ł–ļ–į –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ä—É—Ā—Ć, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
also being the eastern border of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, as well as the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
. The city and its adjacent municipalities constitute Metropolitan BiaŇāystok. The city has a warm summer continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climate, climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and ...
, characterized by warm summers and long frosty winters. Forests are an important part of BiaŇāystok's character and occupy around (18% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth-most forested city in Poland.
The first settlers arrived in the 14th century. A town grew up and received its municipal charter in 1692. BiaŇāystok has traditionally been one of the leading centers of academic, cultural, and artistic life in Podlachia
Podlachia, or Podlasie, ( pl, Podlasie, , be, –ü–į–ī–Ľ—Ź—ą—ą–į, translit=PadliaŇ°Ň°a, uk, –ü—Ė–ī–Ľ—Ź—ą—ą—Ź, translit=Pidliashshia) is a historical region in the north-eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the c ...
and the most important economic center in northeastern Poland. BiaŇāystok was once an important center for light industry
Light industry are industries that usually are less capital-intensive than heavy industry and are more consumer-oriented than business-oriented, as they typically produce smaller consumer goods. Most light industry products are produced for ...
, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The city continues to reshape itself into a modern middle-sized city. BiaŇāystok, in 2010, was on the short-list, but ultimately lost the competition, to become a finalist for European Capital of Culture in 2016.
Etymology
Although nowadays "stok" is translated as "slope", the initial name of the settlement came from the river flowing through it. In old Polish, biaŇāy stok was a clean, swift river (biaŇāy - clean, stok - stream; river that "slides" down the slope). So inconspicuous today, the BiaŇāa River (usually called BiaŇāka), flowing through the city center, gave it its name. Due to changing borders and demographics over the centuries, the city has been known as be, –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ā—ā–ĺ–ļ (''Byelastok'' ?, ''BieŇāastok'' ? ), yi, ◊Ď◊ô◊ź÷∑◊ú◊ô◊°◊ė◊ź÷ł◊ß (''Byalistok'', ''Bjalistok''), lt, Balstogńó, and russian: –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–ĺ—Ā—ā–ĺ–ļ (''Belostok'', ''Byelostok'').History
Archaeological discoveries show that the first settlements in the area of present-day BiaŇāystok occurred during theStone Age
The Stone Age was a broad prehistoric period during which stone was widely used to make tools with an edge, a point, or a percussion surface. The period lasted for roughly 3.4 million years, and ended between 4,000 BC and 2,000 BC, with t ...
. Tombs of ancient settlers can be found in the district of Dojlidy. In the early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, people settled in the area producing kurgan
A kurgan is a type of tumulus constructed over a grave, often characterized by containing a single human body along with grave vessels, weapons and horses. Originally in use on the Pontic‚ÄďCaspian steppe, kurgans spread into much of Central Asi ...
s, the tombs of the chiefs in the area located in the current village of RostoŇāty
RostoŇāty is a village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ra ...
. Since then, the BiaŇāystok area has been at the crossroads of cultures. Trade routes linking the Baltic to the Black Sea favored the development of settlements with Yotvingia
Yotvingia or Sudovia (Yotvingian: ''SŇędava'', lt, Dainava, pl, JańáwieŇľ, german: Sudauen, Eastern Slavic: –Į—Ü—Ć–≤–Ķ–∑—Ć (–Į—ā–≤—Ź–∑—Ć, –ē—ā–≤—Ź–∑—Ć), –Į—ā–≤—Ź–≥–ł—Ź) was a region where the Baltic tribe known as Yotvingians lived. It was lo ...
- Ruthenian-Polish cultural characteristics.
The city of BiaŇāystok has existed for five centuries and during this time the fate of the city has been affected by various political and economic forces.
Surviving documents attest that around 1437 a representative of the Raczk√≥w family, Jakub Tabutowicz of the coat of arms ŇĀabńôdŇļ, received from Michael ŇĹygimantaitis
Michael ŇĹygimantaitis ( lt, Mykolas ŇĹygimantaitis, pl, MichaŇā BolesŇāaw Zygmuntowicz; before 1406 ‚Äď shortly before February 10, 1452 in Moscow) was pretender to the throne of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and the last male descendant of Kńôstu ...
son of Sigismund Kńôstutaitis
Sigismund Kńôstutaitis ( lt, ŇĹygimantas I Kńôstutaitis, pl, Zygmunt Kiejstutowicz; 136520 March 1440) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1432 to 1440. Sigismund was his baptismal name, while his pagan Lithuanian birth name is unknown. He was ...
, Duke of Lithuania, a wilderness area along the river BiaŇāa that marked the beginning of BiaŇāystok as a settlement. BiaŇāystok administratively was part of the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
, after 1569 also part of the Lesser Poland Province of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, includ ...
.
From 1547, the settlement was owned by the WiesioŇāowski family, which founded the first school.Jacek Kusznier, ''Elektrycy w historii Politechniki BiaŇāostockiej'', "Maszyny Elektryczne - Zeszyty Problemowe", Nr 4/2018, p. 163 (in Polish) The first brick church and a castle were built between 1617 and 1826. The two-floor castle, designed on a rectangular plan in the Gothic
Gothic or Gothics may refer to:
People and languages
*Goths or Gothic people, the ethnonym of a group of East Germanic tribes
**Gothic language, an extinct East Germanic language spoken by the Goths
**Crimean Gothic, the Gothic language spoken b ...
-Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
style, was the work of . Extension of the castle was continued by Krzysztof WiesioŇāowski
Krzysztof WiesioŇāowski (died 1637) was a Polish nobleman, starost of Tykocin and SupraŇõl, Stolnik of Lithuania and Ciwun of Wilno before 1620, Court Marshal of Lithuania from 1619, Krajczy of Lithuania from 1620, and Grand Marshal of Lithua ...
, starost
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''—Ā—ā–į—Ä–ĺ—Ā—ā/–į'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. Th ...
of Tykocin, Grand Marshal of Lithuania since 1635, and husband of Aleksandra Marianna Sobieska. In 1637 he died childless, and as a result, BiaŇāystok came under the management of his widow. After her death in 1645 the WiesioŇāowski estate, including BiaŇāystok, passed to the Crown to cover the costs of maintaining Tykocin Castle
The Tykocin Royal Castle is a 15th-century castle located on the right bank of the river Narew in Tykocin, Poland. It fell into ruin in the 18th century and its reconstruction began in 2002.
History
The castle ‚Äď then located on a border area ...
. In the years 1645‚Äď1659 BiaŇāystok was managed by the starost
The starosta or starost (Cyrillic: ''—Ā—ā–į—Ä–ĺ—Ā—ā/–į'', Latin: ''capitaneus'', german: link=no, Starost, Hauptmann) is a term of Slavic origin denoting a community elder whose role was to administer the assets of a clan or family estates. Th ...
s of Tykocin
Tykocin is a small town in north-eastern Poland, with 2,010 inhabitants (2012), located on the Narew river, in BiaŇāystok County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is one of the oldest towns in the region, with its historic center designated a His ...
.
 In 1661 it was given to
In 1661 it was given to Stefan Czarniecki
Stefan Czarniecki (Polish: of the ŇĀodzia coat of arms, 1599 ‚Äď 16 February 1665) was a Polish nobleman, general and military commander. In his career, he rose from a petty nobleman to a magnate holding one of the highest offices in the Commo ...
as a reward for his service in the victory over the Swedes during the Deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the Biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian Comm ...
. Four years later, it was given as a dowry of his daughter Aleksandra, who married Marshal of the Crown Court Jan Klemens Branicki, thus passing into the hands of the Branicki family. In 1692, , the son of Jan Klemens Branicki, obtained city rights for BiaŇāystok from King John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 ‚Äď 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobie ...
. He constructed the Branicki Palace on the foundations of the castle of the WiesioŇāowski family. In the first half of the eighteenth century the ownership of the city was inherited by Field Crown Hetman
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
Jan Klemens Branicki
Count Jan Klemens Branicki (also known as Jan Kazimierz Branicki; 21 September 1689 ‚Äď 9 October 1771) was a Polish nobleman, magnate and Hetman, Field Crown Hetman of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth between 1735 and 1752, and Great Crown ...
. It was he who transformed the palace built by his father into a magnificent residence of a great noble, which was frequently visited by Polish kings and poets. In 1745 the first military technical school in Poland was founded in BiaŇāystok,Jacek Kusznier, ''Elektrycy w historii Politechniki BiaŇāostockiej'', "Maszyny Elektryczne - Zeszyty Problemowe", Nr 4/2018, p. 164 (in Polish) and in 1748, one of the oldest theaters in Poland, the ''Komedialnia'', was founded in the city. New schools were established, including a ballet
Ballet () is a type of performance dance that originated during the Italian Renaissance in the fifteenth century and later developed into a concert dance form in France and Russia. It has since become a widespread and highly technical form of ...
school in connection with the foundation of the theater. In 1749, King Augustus III of Poland
Augustus III ( pl, August III Sas, lt, Augustas III; 17 October 1696 5 October 1763) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1733 until 1763, as well as Elector of Saxony in the Holy Roman Empire where he was known as Frederick Aug ...
extended the city limits. In 1770, under the auspices of Izabella Poniatowska
Countess Izabella Poniatowska (1 July 1730 – 14 February 1808) was a Polish noblewoman, sister of king StanisŇāaw Antoni Poniatowski.
Life
She was the daughter of StanisŇāaw Poniatowski and Konstancja Czartoryska. She was reportedly clo ...
, a midwifery
Midwifery is the health science and health profession that deals with pregnancy, childbirth, and the postpartum period (including care of the newborn), in addition to the sexual and reproductive health of women throughout their lives. In many cou ...
school was founded, based on which the Institute of Obstetrics was established in 1805.
 The end of the eighteenth century saw the
The end of the eighteenth century saw the division
Division or divider may refer to:
Mathematics
*Division (mathematics), the inverse of multiplication
*Division algorithm, a method for computing the result of mathematical division
Military
*Division (military), a formation typically consisting ...
of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
, in three steps, among the neighboring states. The Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Re ...
acquired BiaŇāystok and the surrounding region during the third partition. The city became the capital of the New East Prussia
New East Prussia (german: Neuostpreu√üen; pl, Prusy Nowowschodnie; lt, Naujieji RytprŇęsiai) was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1795 to 1807. It was created out of territory annexed in the Third Partition of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian C ...
province in 1795. Prussia lost the territory following Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 ‚Äď 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's victory in the War of the Fourth Coalition
The Fourth Coalition fought against Napoleon's French Empire and were defeated in a war spanning 1806‚Äď1807. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, s ...
as the resultant 1807 Treaties of Tilsit
The Treaties of Tilsit were two agreements signed by French Emperor Napoleon in the town of Tilsit in July 1807 in the aftermath of his victory at Friedland. The first was signed on 7 July, between Napoleon and Russian Emperor Alexander, when t ...
awarded the area to the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, which organized the region into the Belostok Oblast
Belostok Oblast (russian: –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–ĺ—Ā—ā–ĺ–ļ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ĺ–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—ā—Ć; pl, Obw√≥d biaŇāostocki) was an administrative division in the Russian Empire. The region had a capital in Belostok (modern ''BiaŇāystok'').
History
The oblast was created from f ...
, with the city as the regional center. Schooling and higher learning in BiaŇāystok, which was intensively developed in the 18th century, was stopped as a result of partitions. Later in the 19th century, BiaŇāystok grew into a significant center of the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturi ...
, the largest after ŇĀ√≥dŇļ
ŇĀ√≥dŇļ, also rendered in English as Lodz, is a city in central Poland and a former industrial centre. It is the capital of ŇĀ√≥dŇļ Voivodeship, and is located approximately south-west of Warsaw. The city's coat of arms is an example of canti ...
in then-partitioned Poland. In 1862 a railway connection was launched, connecting BiaŇāystok with Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Grodno
Grodno (russian: –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–ĺ, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–į ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
, Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
and Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, –°–į–Ĺ–ļ—ā-–ü–Ķ—ā–Ķ—Ä–Ī—É—Ä–≥, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ňąsankt p ≤…™t ≤…™rňąburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914‚Äď1924) and later Leningrad (1924‚Äď1991), i ...
. After the failed November
November is the eleventh and penultimate month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian Calendars, the fourth and last of four months to have a length of 30 days and the fifth and last of five months to have a length of fewer than 31 days. No ...
and January
January is the first month of the year in the Julian and Gregorian calendars and is also the first of seven months to have a length of 31 days. The first day of the month is known as New Year's Day. It is, on average, the coldest month of the ...
uprisings, Russification
Russification (russian: —Ä—É—Ā–ł—Ą–ł–ļ–į—Ü–ł—Ź, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cultur ...
policies and anti-Polish
Polonophobia, also referred to as anti-Polonism, ( pl, Antypolonizm), and anti-Polish sentiment are terms for negative attitudes, prejudices, and actions against Poles as an ethnic group, Poland as their country, and their culture. These incl ...
repressions intensified, and after 1870 a ban on the use of Polish in public places was introduced. In 1912, a Tsarist prison was built, which also served as a transit prison for Poles deported to Siberia.
At the end of the nineteenth century, as a result of the influx due to Russian discriminatory regulations, the majority of the city's population was Jewish. According to Russian census of 1897
The first general census of the population of the Russian Empire in 1897 (Russian alphabet#Letters eliminated in 1917–18, pre-reform Russian: ) was the first and only nation-wide census performed in the Russian Empire (the Grand Duchy of Fi ...
, out of the total population of 66,000, Jews constituted 41,900 (so around 63% percent). This heritage can be seen on the Jewish Heritage Trail in BiaŇāystok. The BiaŇāystok pogrom
The Belostok (BiaŇāystok) pogrom occurred between 14‚Äď16 June 1906 (1‚Äď3 June Old Style) in BiaŇāystok, Poland (then part of the Russian Empire). During the pogrom between 81 and 88 people were killed by soldiers of the Imperial Russian Army, ...
occurred between 14 and 16 June 1906 in the city. During the pogrom
A pogrom () is a violent riot incited with the aim of massacring or expelling an ethnic or religious group, particularly Jews. The term entered the English language from Russian to describe 19th- and 20th-century attacks on Jews in the Russia ...
between 81 and 88 Jews
Jews ( he, ◊ô÷į◊Ē◊ē÷ľ◊ď÷ī◊ô◊Ě, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
were killed by the Russians, and about 80 people were wounded.
 .
The first anarchist groups to attract a significant following of Russian workers or peasants were the
.
The first anarchist groups to attract a significant following of Russian workers or peasants were the anarcho-communist
Anarcho-communism, also known as anarchist communism, (or, colloquially, ''ancom'' or ''ancomm'') is a political philosophy and anarchist school of thought that advocates communism. It calls for the abolition of private property but retains resp ...
Chernoe-Znamia
''Chernoe Znamia'' (or Chornoe Znamia) (russian: –ß—Ď—Ä–Ĺ–ĺ–Ķ –∑–Ĺ–į–ľ—Ź, en, The Black Banner), known as the ''Chernoznamentsy'', was a Russian anarchist communist organisation. It emerged in 1903 as a federation of cadres. It took its name, ...
groups, founded in BiaŇāystok in 1903.
 During
During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
the Bialystok-Grodno District
Bialystok-Grodno District (german: link=no, Verwaltungbezirk Bialystok-Grodno) was an administrative division of German-controlled territory of Ober-Ost during World War I (after the Gorlice‚ÄďTarn√≥w Offensive). It was bordered by the Lithuania ...
was the administrative division of German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
-controlled territory of Ober-Ost
, short for ( "Supreme Commander of All German Forces in the East"), was both a high-ranking position in the armed forces of the German Empire as well as the name given to the occupied territories on the German section of the Eastern Front of Wo ...
. It comprised the city, as the capital, and the surrounding Podlaskie region, roughly corresponding to the territory of the earlier Belostok Oblast. At the end of World War I the city became part of the newly independent Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
, as the capital of the BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1919‚Äď1939)
BiaŇāystok Voivodeship ( pl, Wojew√≥dztwo biaŇāostockie) was an administrative unit of interwar Poland (1918‚Äď1939). The province's capital and its biggest city was BiaŇāystok with a population of over 91,000 people. Following the Nazi German an ...
. During the 1919‚Äď1920 Polish‚ÄďSoviet War
The Polish‚ÄďSoviet War (Polish‚ÄďBolshevik War, Polish‚ÄďSoviet War, Polish‚ÄďRussian War 1919‚Äď1921)
* russian: –°–ĺ–≤–Ķ—ā—Ā–ļ–ĺ-–Ņ–ĺ–Ľ—Ć—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –≤–ĺ–Ļ–Ĺ–į (''Sovetsko-polskaya voyna'', Soviet-Polish War), –ü–ĺ–Ľ—Ć—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ —Ą—Ä–ĺ–Ĺ—ā (' ...
, possession of the city by the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: –†–į–Ī–ĺŐĀ—á–Ķ-–ļ—Ä–Ķ—Ā—ā—Ć—ŹŐĀ–Ĺ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ö—Ä–įŐĀ—Ā–Ĺ–į—Ź –į—Ä–ľ–ł—Ź),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
and the Provisional Polish Revolutionary Committee
Provisional Polish Revolutionary Committee ( pl, Tymczasowy Komitet Rewolucyjny Polski, Polrewkom; russian: –ü–ĺ–Ľ—Ć—Ä–Ķ–≤–ļ–ĺ–ľ) (July‚ÄďAugust 1920) was a revolutionary committee created under the patronage of Soviet Russia with the goal to e ...
occurred during the lead up to the Battle of Warsaw. During the resultant counteroffensive, the city returned to Polish control after the Battle of BiaŇāystok
The Battle of BiaŇāystok was a battle of the Polish‚ÄďSoviet War that took place near and in BiaŇāystok, Poland, on August 22, 1920, between the 1st Legions Infantry Regiment and the remains of the Soviet Russian Red Army 16th Army group and ...
.
After the wars and the reestablishment of independent Poland, Polish education in BiaŇāystok was restored and the textile industry was revived. A municipal public library was established, sports clubs were founded, including Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok
Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok () is a Polish football club based in BiaŇāystok that plays in the Ekstraklasa, the top level of Polish football. The club was founded in 1920 by soldiers in the Reserve Battalion in BiaŇāystok. Jagiellonia play their home g ...
, and in the 1930s a drama theater was built.
 With the beginning of
With the beginning of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
, Poland was invaded by Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
. Initially BiaŇāystok was briefly occupied
' (Norwegian: ') is a Norwegian political thriller TV series that premiered on TV2 on 5 October 2015. Based on an original idea by Jo Nesb√ł, the series is co-created with Karianne Lund and Erik Skjoldbj√¶rg. Season 2 premiered on 10 October 2 ...
by Germany, and the German '' Einsatzgruppe IV'' entered the city on September 20‚Äď21, 1939 to commit crimes against the population. Afterwards, the Germans handed the city over to the Soviet Union, as a result of the Molotov‚ÄďRibbentrop Pact
, long_name = Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
, image = Bundesarchiv Bild 183-H27337, Moskau, Stalin und Ribbentrop im Kreml.jpg
, image_width = 200
, caption = Stalin and Ribbentrop shaking ...
. Under Soviet occupation, it was incorporated into the Byelorussian SSR
The Byelorussian Soviet Socialist Republic (BSSR, or Byelorussian SSR; be, –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ä—É—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –°–į–≤–Ķ—Ü–ļ–į—Ź –°–į—Ü—č—Ź–Ľ—Ė—Ā—ā—č—á–Ĺ–į—Ź –†—ć—Ā–Ņ—É–Ī–Ľ—Ė–ļ–į, Bielaruskaja Savieckaja Sacyjalistyńćnaja Respublika; russian: –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–ĺ—Ä— ...
from 1939 to 1941 as the capital of Belastok Region
Belastok Voblast or Belostok Oblast ( be, –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ā—ā–ĺ—Ü–ļ–į—Ź –≤–ĺ–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—Ü—Ć, BieŇāastockaja vobŇāasńá, russian: –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–ĺ—Ā—ā–ĺ–ļ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ě–Ī–Ľ–į—Ā—ā—Ć, pl, Obw√≥d biaŇāostocki) was a short-lived territorial unit in the Belarusian Soviet ...
. Polish people were subject to deportations deep into the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
(Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, –°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć, r=Sibir', p=s ≤…™ňąb ≤ir ≤, a=Ru-–°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Far North). Pre-war mayor Seweryn Nowakowski was arrested by the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: –Ě–į—Ä–ĺŐĀ–ī–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ļ–ĺ–ľ–ł—Ā—Ā–į—Ä–ł–įŐĀ—ā –≤–Ĺ—ÉŐĀ—ā—Ä–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ–ł—Ö –ī–Ķ–Ľ, Nar√≥dnyy komissari√°t vn√ļtrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
in October 1939 and probably also deported to the USSR, however his fate remains unknown. The NKVD took over the local prison. The Polish resistance movement was active in the city, which was the seat of one of the six main commands of the Union of Armed Struggle
ZwińÖzek Walki Zbrojnej ( abbreviation: ''ZWZ''; Union of Armed Struggle;Thus rendered in Norman Davies, ''God's Playground: A History of Poland'', vol. II, p. 464. also translated as ''Union for Armed Struggle'', ''Association of Armed Strug ...
in occupied Poland (alongside Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
, Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
, PoznaŇĄ
PoznaŇĄ () is a city on the River Warta in west-central Poland, within the Greater Poland region. The city is an important cultural and business centre, and one of Poland's most populous regions with many regional customs such as Saint John ...
, ToruŇĄ
)''
, image_skyline =
, image_caption =
, image_flag = POL ToruŇĄ flag.svg
, image_shield = POL ToruŇĄ COA.svg
, nickname = City of Angels, Gingerbread city, Copernicus Town
, pushpin_map = Kuyavian-Pom ...
and Lwów
Lviv ( uk, –õ—Ć–≤—Ė–≤) is the largest city in western Ukraine, and the seventh-largest in Ukraine, with a population of . It serves as the administrative centre of Lviv Oblast and Lviv Raion, and is one of the main cultural centres of Ukraine ...
). BiaŇāystok native and future President of Poland in exile In Exile may refer to:
Film and television
* ''In Exile'' (film) or ''Time Runner'', a 1993 science fiction film
* ''In Exile'' (TV series), a 1998 UK sitcom
Literature
* "In Exile" (short story), an 1892 short story by Anton Chekhov
*''In Exile'' ...
Ryszard Kaczorowski
Ryszard Kaczorowski, GCMG (; 26 November 1919 ‚Äď 10 April 2010) was a Polish statesman. From 1989 to 1990, he served as the last President of Poland- in-exile. He succeeded Kazimierz Sabbat, and resigned his post following Poland's regaini ...
was a member of the local Polish resistance and was arrested in the city by the NKVD in 1940. Initially the Soviets sentenced him to death, but eventually he was sentenced to 10 years in forced labor camps
''Forced'' is a single-player and co-op action role-playing game developed by BetaDwarf, released in October 2013 for Windows, OS X and Linux through the Steam platform as well as Wii U. It is about gladiators fighting for their freedom in a fan ...
and deported to Kolyma
Kolyma (russian: –ö–ĺ–Ľ—č–ľ–įŐĀ, ) is a region located in the Russian Far East. It is bounded to the north by the East Siberian Sea and the Arctic Ocean, and by the Sea of Okhotsk to the south. The region gets its name from the Kolyma River an ...
, from where he was released in 1942, when he joined the Anders' Army
Anders' Army was the informal yet common name of the Polish Armed Forces in the East in the 1941‚Äď42 period, in recognition of its commander WŇāadysŇāaw Anders. The army was created in the Soviet Union but, in March 1942, based on an understandi ...
.
In the course of the German invasion of the Soviet Union
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
in 1941, BiaŇāystok was occupied by the German Army
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the ''Luftwaf ...
on 27 June 1941, during the Battle of BiaŇāystok‚ÄďMinsk
The Battle of BiaŇāystok‚ÄďMinsk was a German strategic operation conducted by the Wehrmacht's Army Group Centre under Field Marshal Fedor von Bock during the penetration of the Soviet border region in the opening stage of Operation Barbarossa, ...
, and the city became the capital of Bezirk BiaŇāystok
Bialystok District (German language, German: ''Bezirk Bialystok'') was an administrative unit of Nazi Germany created during the World War II invasion of the Soviet Union. It was to the south-east of East Prussia, in present-day northeastern Poland ...
, a separate region in German occupied Poland
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
, until 1944. The Great Synagogue was burnt down by Germans on June 27, 1941, with an estimated number of 2,000 Jews inside. From the very beginning, the Nazis pursued a ruthless policy of pillage and removal of the non-German population. The Germans operated a Nazi prison in the city, and a forced labour
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
camp for Jewish men. Since 1943, the ''Sicherheitspolizei
The ''Sicherheitspolizei'' ( en, Security Police), often abbreviated as SiPo, was a term used in Germany for security police. In the Nazi era, it referred to the state political and criminal investigation security agencies. It was made up by the ...
'' carried out deportations of Poles including teenage boys from the local prison to the Stutthof concentration camp
Stutthof was a Nazi concentration camp established by Nazi Germany in a secluded, marshy, and wooded area near the village of Stutthof (now Sztutowo) 34 km (21 mi) east of the city of Danzig (GdaŇĄsk) in the territory of the German-a ...
. The 56,000 Jewish residents of the town were confined in a ghetto. On August 15, 1943, the BiaŇāystok Ghetto Uprising
BiaŇāystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
BiaŇāystok is located in the BiaŇāystok Up ...
began, and several hundred Polish Jews
The history of the Jews in Poland dates back at least 1,000 years. For centuries, Poland was home to the largest and most significant Ashkenazi Jewish community in the world. Poland was a principal center of Jewish culture, because of the lo ...
and members of the Anti-Fascist Military Organisation
Antyfaszystowska Organizacja Bojowa (Polish for ''Anti-Fascist Military Organisation''), AOB, was an underground organization formed in 1942 in the Ghetto in BiaŇāystok by former officers of the Polish Land Forces. It took part in the BiaŇāystok G ...
( pl, Antyfaszystowska Organizacja Bojowa) started an armed struggle against the German troops who were carrying out the planned liquidation of the ghetto with deportations to the Treblinka extermination camp
Treblinka () was an extermination camp, built and operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland during World War II. It was in a forest north-east of Warsaw, south of the village of Treblinka in what is now the Masovian Voivodeship. The camp ...
.
The city fell under the control of the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: –†–į–Ī–ĺŐĀ—á–Ķ-–ļ—Ä–Ķ—Ā—ā—Ć—ŹŐĀ–Ĺ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ö—Ä–įŐĀ—Ā–Ĺ–į—Ź –į—Ä–ľ–ł—Ź),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
on 27 July 1944. The Soviets carried out mass arrests of Polish resistance members in the city and region, and imprisoned them in BiaŇāystok. On 20 September 1944 the city was transferred back to Poland, although with a Soviet-installed communist regime, which stayed in power until the Fall of Communism
The Revolutions of 1989, also known as the Fall of Communism, was a revolutionary wave that resulted in the end of most communist states in the world. Sometimes this revolutionary wave is also called the Fall of Nations or the Autumn of Natio ...
in the 1980s, and the Soviet NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: –Ě–į—Ä–ĺŐĀ–ī–Ĺ—č–Ļ –ļ–ĺ–ľ–ł—Ā—Ā–į—Ä–ł–įŐĀ—ā –≤–Ĺ—ÉŐĀ—ā—Ä–Ķ–Ĺ–Ĺ–ł—Ö –ī–Ķ–Ľ, Nar√≥dnyy komissari√°t vn√ļtrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
and SMERSH
SMERSH (russian: –°–ú–ē–†–®) was an umbrella organization for three independent counter-intelligence agencies in the Red Army formed in late 1942 or even earlier, but officially announced only on 14 April 1943. The name SMERSH was coined by Josep ...
continued the persecution of the Polish resistance in the following months. From November 1944 to January 1945, the Russians deported nearly 5,000 Poles from the local prison to the Soviet Union. Later on, the Soviet-appointed communists held political prisoners and other members of the Polish resistance in the local prison, and until 1956, they also carried out burials of executed Polish resistance members there.
After the war, the city became capital of the initial BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1945‚Äď1975) BiaŇāystok Voivodeship may refer to the following administrative districts of Poland:
* BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1919‚Äď1939), as defined before World War II
* BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1945‚Äď1975), as defined after World War II
*BiaŇāystok Voivodesh ...
of the People's Republic of Poland
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million nea ...
. After the 1975 administrative reorganization, the city was the capital of the smaller BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1975‚Äď1998)
BiaŇāystok Voivodeship ( pl, Wojew√≥dztwo biaŇāostockie) was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland from 1975 to 1998, when it was superseded by the Podlaskie Voivodeship. Its capital city was BiaŇāystok. It was formed ...
. Since 1999 it has been the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
, Republic of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
.
Geography
Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
.It is the biggest Polish city close to Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, –†–Ķ—Ā–Ņ—É–Ī–Ľ–ł–ļ–į –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ä—É—Ā—Ć, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. The BiaŇāa River, a left tributary of the SupraŇõl River, passes through the city. The landscape of the BiaŇāystok Upland is diverse, with high moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice shee ...
hills and kame
A kame, or ''knob'', is a glacial landform, an irregularly shaped hill or mound composed of sand, gravel and till that accumulates in a depression on a retreating glacier, and is then deposited on the land surface with further melting of the g ...
in excess of above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
. Vast areas of outwash
An outwash plain, also called a sandur (plural: ''sandurs''), sandr or sandar, is a plain formed of glaciofluvial deposits due to meltwater outwash at the terminus of a glacier. As it flows, the glacier grinds the underlying rock surface and ca ...
, a glacial
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
plain
In geography, a plain is a flat expanse of land that generally does not change much in elevation, and is primarily treeless. Plains occur as lowlands along valleys or at the base of mountains, as coastal plains, and as plateaus or uplands ...
formed of sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
s deposited by meltwater at the terminus of a glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires dis ...
, are covered by forests.
The highest point of the city lies at a height of on the Pietrasze Forest. The lowest point lies at a height of on the river valley of the BiaŇāa.
Forests are an important part of the city character, they currently occupy approximately (18% of the administrative area of the city) which places it as the fifth most "wooded" city in Poland; behind Katowice (38%), Bydgoszcz (30%), ToruŇĄ (22.9%) and GdaŇĄsk (17.6%).
Part of Knyszyn Forest is preserved within the city limits by two nature reserves
A nature reserve (also known as a wildlife refuge, wildlife sanctuary, biosphere reserve or bioreserve, natural or nature preserve, or nature conservation area) is a protected area of importance for flora, fauna, or features of geological or o ...
‚ÄĒa total area of . The Zwierzyniecki Forest Nature Reserve ( pl, Rezerwat przyrody Las Zwierzyniecki), which is contained within the city limits, is a fragment, , of the riparian forest
A riparian forest or riparian woodland is a forested or wooded area of land adjacent to a body of water such as a river, stream, pond, lake, marshland, estuary, canal, sink or reservoir.
Etymology
The term riparian comes from the Latin word '' ...
with a dominant assemblage of oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
and hornbeam
Hornbeams are hardwood trees in the flowering plant genus ''Carpinus'' in the birch family Betulaceae. The 30‚Äď40 species occur across much of the temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere.
Origin of names
The common English name ''hornbeam' ...
. The Antoniuk Nature Reserve ( pl, Rezerwat Przyrody Antoniuk) is a park in the city that preserves the natural state of a forest fragment characteristic of the BiaŇāystok Upland, with a dominant mixed forest of hazel
The hazel (''Corylus'') is a genus of deciduous trees and large shrubs native to the temperate Northern Hemisphere. The genus is usually placed in the birch family Betulaceae,Germplasmgobills Information Network''Corylus''Rushforth, K. (1999). ...
and spruce
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
.
The of forests lying in the vicinity of the Dojlidy Ponds are administered by the BiaŇāystok Central Sports and Recreation Center( pl, BiaŇāostocki OŇõrodek Sportu i Rekreacji ‚Äď BOSiR). The Dojlidy Ponds recreation area includes a public beach, walking trails, birdwatching and fishing.
Climate
The city has a warm-summer continental orhemiboreal
Hemiboreal means halfway between the temperate and subarctic (or boreal) zones. The term is most frequently used in the context of climates and ecosystems.
Botany
A hemiboreal forest has some characteristics of a boreal forest to the north, and ...
climate (''Dfb'') according to the Köppen climate classification
The K√∂ppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir K√∂ppen (1846‚Äď1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by K√∂ppen, notabl ...
system under the isotherm for the average temperature of the coldest month, or an oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(''Cfb'') if the isotherm is used. The city would have been classified as being in the ''Dfb'' zone regardless of the accepted isotherm for climatological normal
Climatological normal or climate normal (CN) is a 30-year average of a weather variable for a given time of year. a consequence of
 The city of BiaŇāystok is divided into 29 administrative units, known in
The city of BiaŇāystok is divided into 29 administrative units, known in  The city covers of which is
The city covers of which is
It is also the seat of government for the
 The 18th Reconnaissance Regiment ( pl, 18 PuŇāk Rozpoznawczy) of the
The 18th Reconnaissance Regiment ( pl, 18 PuŇāk Rozpoznawczy) of the
 In the nineteenth century, BiaŇāystok was an important center for light industry, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The tradition continued with many garment factories established in the twentieth century, such as ''Fasty'' in the district of Bacieczki. However, after the fall of communism in 1989 many of these factories faced severe problems and subsequently closed down.
The unemployment rate for November 2020 in BiaŇāystok was 6.8%.
The 2009 average household had a monthly per capita income of 1018.77 zŇā and monthly per capita expenses of 823.56 zŇā
The city has a number of nearby border crossings. The border with Belarus is only away, the nearest border crossings are located in;
In the nineteenth century, BiaŇāystok was an important center for light industry, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The tradition continued with many garment factories established in the twentieth century, such as ''Fasty'' in the district of Bacieczki. However, after the fall of communism in 1989 many of these factories faced severe problems and subsequently closed down.
The unemployment rate for November 2020 in BiaŇāystok was 6.8%.
The 2009 average household had a monthly per capita income of 1018.77 zŇā and monthly per capita expenses of 823.56 zŇā
The city has a number of nearby border crossings. The border with Belarus is only away, the nearest border crossings are located in; 
 The leading industries in the city's economy are food processing (production of meat products, fruit and vegetable products, the production of
The leading industries in the city's economy are food processing (production of meat products, fruit and vegetable products, the production of
 BiaŇāystok is one of the largest cultural centers in the
BiaŇāystok is one of the largest cultural centers in the
 There are a number of museums in the city including:
The Historical Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Historyczne w BiaŇāymstoku) is part of the Podlaskie Museum. The facility has a rich collection of archival materials and
There are a number of museums in the city including:
The Historical Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Historyczne w BiaŇāymstoku) is part of the Podlaskie Museum. The facility has a rich collection of archival materials and  The Army Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Wojska w BiaŇāymstoku) was established in September 1968 as a branch of the Podlaskie Museum to house the research and collections of many people connected with the military history of north-eastern Poland.
The Army Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Wojska w BiaŇāymstoku) was established in September 1968 as a branch of the Podlaskie Museum to house the research and collections of many people connected with the military history of north-eastern Poland.
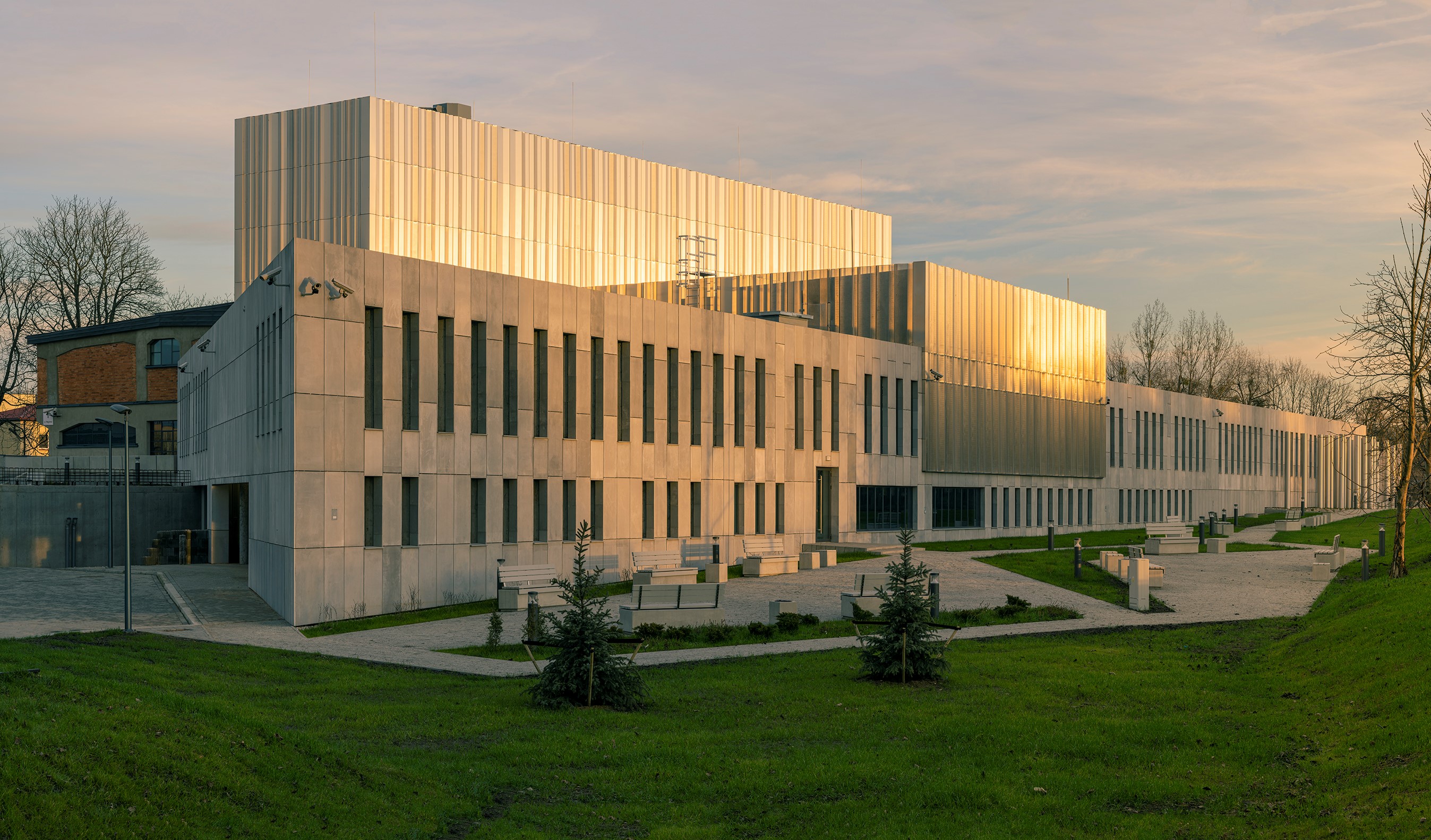 The Sybir Memorial Museum ( pl, Muzeum Pamińôci Sybiru) is a historical museum opened in 2021 and dedicated to the memory of Poles as well as people from other nationalities who were the victims of forced deportations to
The Sybir Memorial Museum ( pl, Muzeum Pamińôci Sybiru) is a historical museum opened in 2021 and dedicated to the memory of Poles as well as people from other nationalities who were the victims of forced deportations to
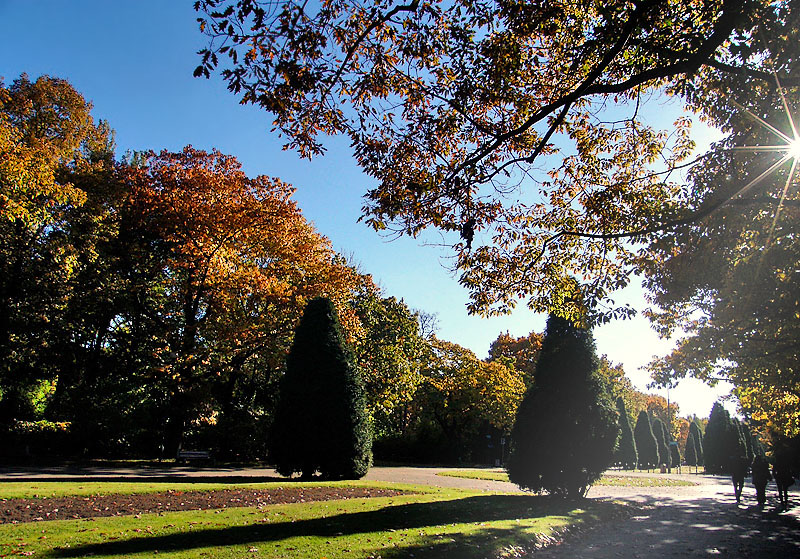 Around 32% of the city is occupied by parks, squares and forest preserves which creates a unique and healthy climate. The green spaces include:
Branicki Palace ( pl, PaŇāac Branickich) is a historical edifice and park in BiaŇāystok. It was developed on the site of an earlier building in the first half of the eighteenth century by
Around 32% of the city is occupied by parks, squares and forest preserves which creates a unique and healthy climate. The green spaces include:
Branicki Palace ( pl, PaŇāac Branickich) is a historical edifice and park in BiaŇāystok. It was developed on the site of an earlier building in the first half of the eighteenth century by
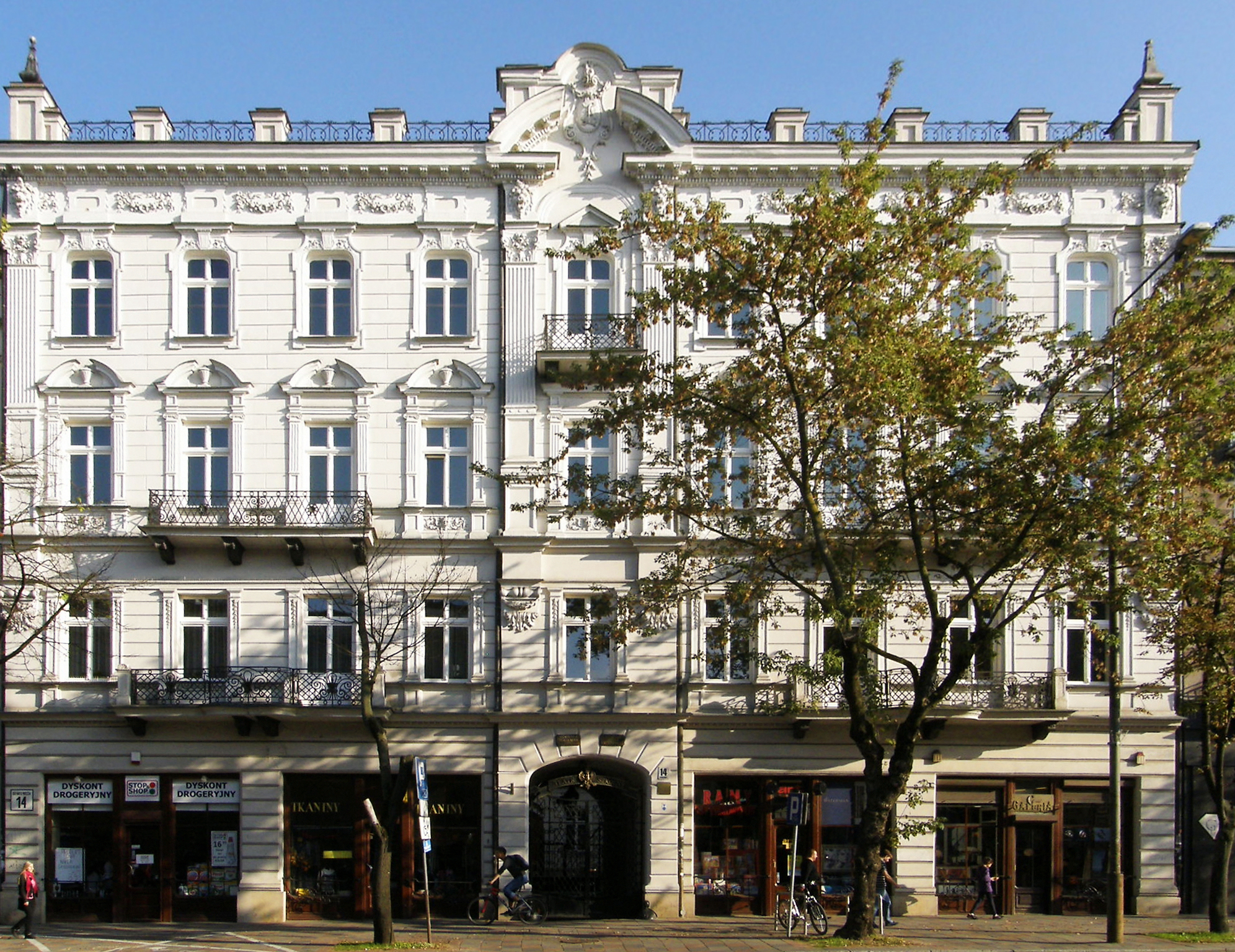 The various historically driven changes have had a very significant influence on the architectural space of the city. Most other Polish cities have suffered similarly, but the processes in BiaŇāystok, have had a particularly intense course. Numerous historic works of architecture no longer exist, while many others have been rebuilt to their original configuration. Very few historic buildings of the city have been preserved ‚Äď the sights are merely an echo of the old historical shape of BiaŇāystok.
Main sights include:
* Palaces: Branicki Palace, Branicki Guest Palace, Lubomirski Palace, Hasbach Palace, Nowik Palace
* Townhall
* Catholic Cathedral
* St. Roch Church
* St. Adalbert Church
* Orthodox Cathedral
* Daughters of Charity Monastery
* Former Arsenal
* Former Masonic Lodge
The various historically driven changes have had a very significant influence on the architectural space of the city. Most other Polish cities have suffered similarly, but the processes in BiaŇāystok, have had a particularly intense course. Numerous historic works of architecture no longer exist, while many others have been rebuilt to their original configuration. Very few historic buildings of the city have been preserved ‚Äď the sights are merely an echo of the old historical shape of BiaŇāystok.
Main sights include:
* Palaces: Branicki Palace, Branicki Guest Palace, Lubomirski Palace, Hasbach Palace, Nowik Palace
* Townhall
* Catholic Cathedral
* St. Roch Church
* St. Adalbert Church
* Orthodox Cathedral
* Daughters of Charity Monastery
* Former Arsenal
* Former Masonic Lodge
File:Ratusz 5.07.2012.jpg, KoŇõciuszko Square with the Town Hall
File:BiaŇāystok - KoŇõci√≥Ňā Ňõw. Rocha - 2016-09-09 15-25-34.jpg, Church of St. Roch
File:Adalbert of Prague church in BiaŇāystok.jpg, St. Adalbert Church
File:150913 Lubomirski Palace in BiaŇāystok - 03.jpg, Lubomirski Palace
File:KsińÖŇľnica Podlaska.JPG, Former Masonic Lodge
File:BiaŇāystok Dojlidy Fabryczne 23, PaŇāac Hasbacha.jpg, Hasbach Palace
 BiaŇāystok has a wide variety of media outlets serving the city and surrounding region. There are two locally published daily newspapers,
BiaŇāystok has a wide variety of media outlets serving the city and surrounding region. There are two locally published daily newspapers,
File:BiaŇāystok- Stary KoŇõci√≥Ňā Farny (wiosna 2009).JPG, Old Parish Church
File:BiaŇāystok katedra 3.JPG, Basilica of the Assumption of the Blessed Virgin Mary
File:Statua Jezusa przy koŇõciele Zmartwychwstania PaŇĄskiego w BiaŇāymstoku 2.jpg, Church of the Resurrection
File:Podlaskie - BiaŇāystok - BiaŇāystok - Antoniuk Fabryczny 45 - KoŇõci√≥Ňā Wszystkich Ňöwińôtych - Front.JPG, All Saints' Church
File:Cerkiew Ňöwińôtego Ducha BiaŇāystok.JPG,
 The city is and has been for centuries, the main hub of transportation for the
The city is and has been for centuries, the main hub of transportation for the
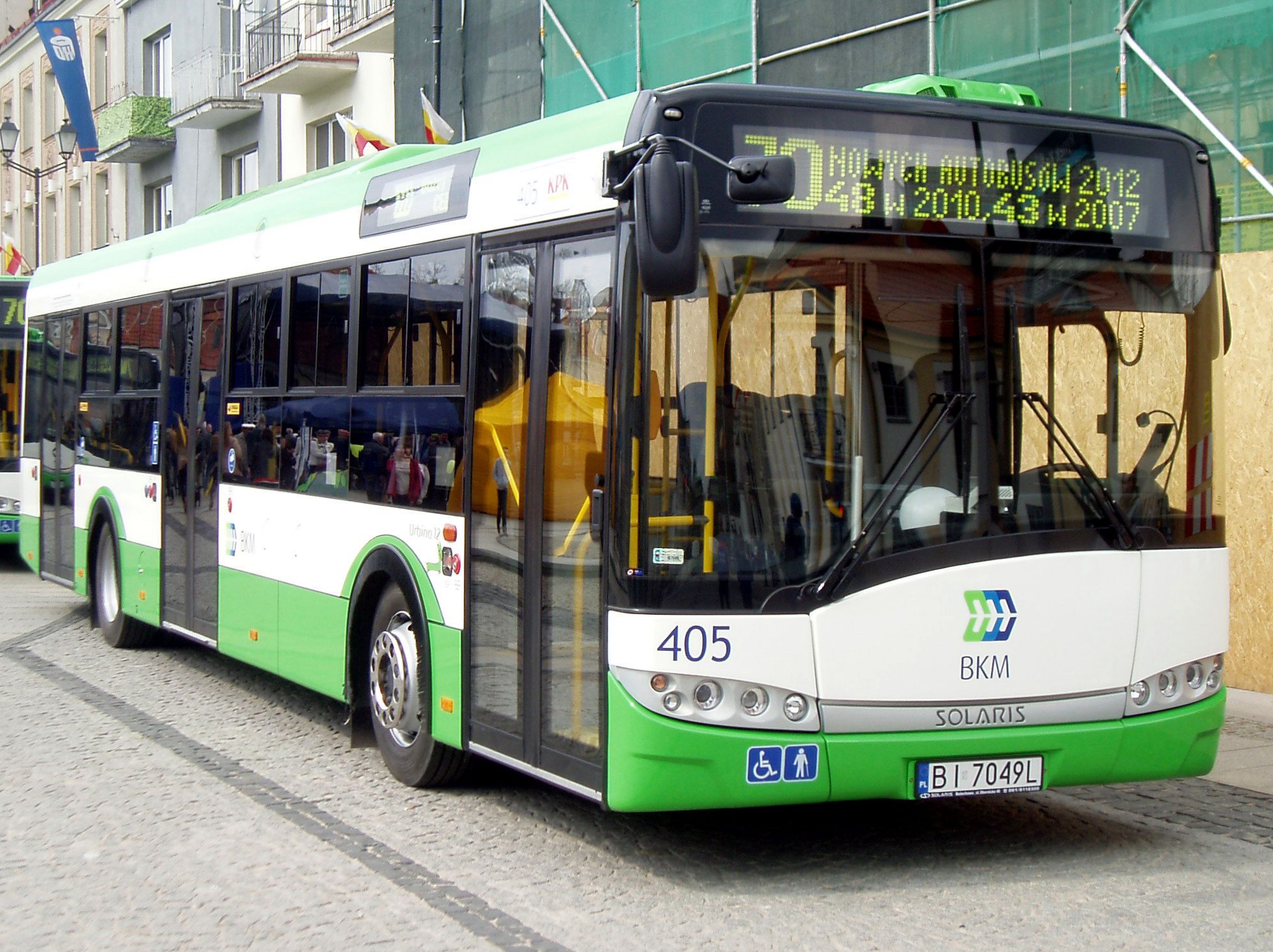

 Higher education in the city can be traced back to the second half of the eighteenth century when the ownership of the city was inherited by
Higher education in the city can be traced back to the second half of the eighteenth century when the ownership of the city was inherited by
 Over the centuries, a number of people from BiaŇāystok have been prominent in the fields of science, language, politics, religion, sports, visual arts and performing arts. This environment was created in the mid-eighteenth century by the patronage of
Over the centuries, a number of people from BiaŇāystok have been prominent in the fields of science, language, politics, religion, sports, visual arts and performing arts. This environment was created in the mid-eighteenth century by the patronage of
Trzy procent odmiennoŇõci
(Three percent of different) ‚Äď article describing results of Polish census 2002 and minorities in Poland, citing census data * Janusz ŇĽarnowski, ''"SpoŇāeczeŇĄstwo Drugiej Rzeczypospolitej 1918‚Äď1939"'', Warszawa 1973 * Eugeniusz Mironowicz, ''"BiaŇāoruŇõ"'', Trio, Warszawa, 1999, * Yvette Walczak, ''"Let Her Go!"'', Naomi Roth Publishing, London, 2012,
Osiedla.BiaŇāystok.pl
VisitBiaŇāystok.com
*
Official Site BiaŇāystok City Transport
Google Transit in BiaŇāystok
*
BiaŇāystok
at the B&F Compendium of Jewish Genealogy {{DEFAULTSORT:Bialystok Cities and towns in Podlaskie Voivodeship City counties of Poland Cities with powiat rights Podlachian Voivodeship Belostoksky Uyezd BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1919‚Äď1939) Belastok Region Holocaust locations in Poland Jewish communities destroyed in the Holocaust
climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming‚ÄĒthe ongoing increase in global average temperature‚ÄĒand its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. BiaŇāystok is one of the coldest cities in Poland by annual temperature and one with the climate having the most continental characteristics, as is the case for much of north-eastern Poland, with the mean yearly temperature of and the length of the growing season
A season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The growing season is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal plant growth. Whil ...
amounting to 205 days, shorter than elsewhere in Poland.
While winters are rather mild compared to other cities on the similar latitude, such as Samara
Samara ( rus, –°–į–ľ–įŐĀ—Ä–į, p=s…źňąmar…ô), known from 1935 to 1991 as Kuybyshev (; ), is the largest city and administrative centre of Samara Oblast. The city is located at the confluence of the Volga and the Samara (Volga), Samara rivers, with ...
, Barnaul
Barnaul ( rus, –Ď–į—Ä–Ĺ–į—ÉŐĀ–Ľ, p=b…ôrn…źňąul) is the largest types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and administrative centre of Altai Krai, Russia, located at the confluence of the Barnaulka and Ob Rivers in the West Siberian Plain. As ...
, or Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
, they are relatively cold by Polish standards and colder still than in Western Europe
Western Europe is the western region of Europe. The region's countries and territories vary depending on context.
The concept of "the West" appeared in Europe in juxtaposition to "the East" and originally applied to the ancient Mediterranean ...
(in cities like Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
and Dublin
Dublin (; , or ) is the capital and largest city of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. On a bay at the mouth of the River Liffey, it is in the Provinces of Ireland, province of Leinster, bordered on the south by the Dublin Mountains, a part of th ...
). They are usually rather cold with little sunshine, with weather patterns changing from those influenced by the low-pressure systems generated by the Icelandic Low
The Icelandic Low is a semi-permanent centre of low atmospheric pressure found between Iceland and southern Greenland and extending in the Northern Hemisphere winter into the Barents Sea. In the summer, it weakens and splits into two centres, one ...
(when the weather is often cloudy, cool, damp, rainy and/or snowy) to the occasional intrusions of cold air masses from Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, –°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć, r=Sibir', p=s ≤…™ňąb ≤ir ≤, a=Ru-–°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
or the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
(Siberian High
The Siberian High (also Siberian Anticyclone; russian: –ź–∑–ł–į—ā—Ā–ļ–ł–Ļ –į–Ĺ—ā–ł—Ü–ł–ļ–Ľ–ĺ–Ĺ (''Aziatsky antitsiklon'')) is a massive collection of cold dry air that accumulates in the northeastern part of Eurasia from September until April. It ...
), which, due to the city's northeasterly location, are more frequent than in other parts of Poland. Winters thus tend to be several degrees colder than elsewhere in Poland. Freezing conditions below are possible in winter but are rare. Snow cover is present on the ground for more than half of winter. Summers tend to be warm, sunny and pleasant and are occasionally hot, but they are still a little cooler than in most of Poland. More rain falls in summer months than in any other period of the year.
The centre of BiaŇāystok, as most urban areas, experiences the urban heat island effect
An urban heat island (UHI) is an urban or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent w ...
, therefore for most of the time, the city is warmer than the surrounding countryside. The temperatures in the city centre are, on average, higher than in the surrounding villages, with greater differences at night and during the warmer half of the year, particularly in spring.
Urban layout
Bialystok is roughly circular, centered around the old city Church Square and Branicki Palace. Originally, the city's territory was about 50 hectares. The communication system serving the entire city was made of streets radiating out from the central market square. An inventory plan made by Becker in 1799 was needed by the Prussian authorities in connection with the negotiations on the acquisition of BiaŇāystok for a royal residence. The plan is of fundamental importance as it shows the development of the city in the first period of its creation. The area of ‚Äč‚Äčthe city did not exceed 1.5 km2, and the population was approx. 3.5 thousand. The entire urban area was closed with 6 loose-fitting gates and buildings situated on regular plots. Compact buildings were found only in the market square, the frontages of which were 1- 2-storey buildings with brick front elevations. Choroska and Zamkowa Streets were built up with only brick houses. The city was dominated by the palace complex, which, together with the park, covered an area equal to the city's investment areas. The residence palace was designed on a European scale and created new development opportunities for BiaŇāystok. After the First World War, the first attempts were made to organize the city, which had so far developed without plans - between the palace grounds and arable land. At the request of the Association of Polish Cities, in the years 1938-1939 a general urban concept of the city was created by Ignacy TŇāoczek. The plan called for the creation of new communication routes, relieve the center, demolish the Chanajki district, create a housing estate and connect with it the unique green areas around the city with new tree plantings. The Second World War prevented the comprehensive implementation of this plan. As a result of war damage, many buildings partially or completely destroyed, especially at the city center. The reconstruction of the town began with the restoration of the activity of textile factories. It was conditioned by the desire to improve the economic situation of the city as quickly as possible. The average height of buildings in the city is not high. The center is dominated by buildings not exceeding 25 meters in height, and the outskirts of the city are mainly occupied by low-rise single-family houses. Taller buildings dominate in two residential districts. They are the districts of Piasta (located to the south of the city center) and the Dziesińôciny estate (located to the northwest of the city center). Dominants in BiaŇāystok are located mainly in the center and they are also there located two most important city icons: the Church of St. Roch and the Parish Church, which are on one axis. Each of the districts also has its dominant, which is usually a church or an Orthodox church. The most important space in the city is KoŇõciuszko Square - the main square in the shape of a triangle. The space is delimited by two axes, one is part of the axis connecting the two largest churches, and the other runs towards the west of the Center district along Suraska Street and ends at MŇāynowa Street. An important spatial arrangement in BiaŇāystok is the Branicki Palace complex. The baroque layout of the palace complex is symmetrically shaped according to one compositional axis with a coherent garden layout. Throughout the years it expanded to include nearby villages: In the mid-eighteenth century Bojary which was located on the right bank of the Biala River was incorporated to it. On May 10, 1919, in accordance with the decision of the Sejm, Bialostoczek, Horodniany, Zwierzyniec-Letnisko, Starosielce, SŇāoboda (which was founded at the end of the 17th century, between the current Pogodna and Ňöwierkowa Streets), Ogrodniki, Pieczurki, Wysoki Stoczek were incorporated also, as well as two mill villages Marczuk and Antoniuk. By the onset ofWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
the city's territory amounted to 40 km2. The reconstruction of the city following the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
and establishment of the People's Republic of Poland
The Polish People's Republic ( pl, Polska Rzeczpospolita Ludowa, PRL) was a country in Central Europe that existed from 1947 to 1989 as the predecessor of the modern Republic of Poland. With a population of approximately 37.9 million nea ...
saw further expansion: the villages Bacieczki, Bacieczki Kolonia, Korycin
Korycin is a village in Sok√≥Ňāka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Korycin. It lies approximately west of Sok√≥Ňāka
Sok√≥Ňāka (; lt, Sokulka, Sakali ...
and part of the village Klepacze, Krupniki
Krupniki is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Choroszcz, within BiaŇāystok County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It lies approximately east of Choroszcz and north-west of the regional capital BiaŇāystok
BiaŇā ...
, Fasty
Fasty is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Dobrzyniewo DuŇľe, within BiaŇāystok County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland. It lies approximately south-east of Dobrzyniewo DuŇľe and north-west of the regional capit ...
, ZaŇõcianki and Zawady were incorporated into the city. The 70s saw another wave of expansion with the villages of Bagn√≥wka, area of ZakŇāady Silikatowe, areas of state forests, Dojlidy ponds and the orthodox cemetery at Dojlidy. At the onset of the millennium, in 2002, the village Zawady was included in the city's limits and at the last enlargement, in 2006, the villages Dojlidy G√≥rne, Zag√≥rki and Kolonia Halickie were incorporated and the city reached its current territory of 102 km2.
Districts
 The city of BiaŇāystok is divided into 29 administrative units, known in
The city of BiaŇāystok is divided into 29 administrative units, known in Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles, people from Poland or of Polish descent
* Polish chicken
*Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwr ...
as '' osiedla''. The first 27 of these were created on October 25, 2004. The 28th, Dojlidy Górne, was created by on October 23, 2006, out of three settlements which had been incorporated into the city: Dojlidy Górne, Kolonia Halickie, and Zagórki. A new district called Bagnówka was created at the beginning of 2021.
The center of the city, Osiedle Centrum, surrounds Lipowa Street, the main street of the city. Lipowa Street extends from Rynek KoŇõciuszki (the corner of Sp√≥Ňādzielcza Street) to Plac NiepodlegŇāoŇõci im. Romana Dmowskiego (the corner of Krakowska Street). Over the centuries the name of this street has taken on a number of different names; Choroska, Nowolipie, Lipowa, J√≥zef PiŇāsudski
), Vilna Governorate, Russian Empire (now Lithuania)
, death_date =
, death_place = Warsaw, Poland
, constituency =
, party = None (formerly PPS)
, spouse =
, children = Wan ...
, Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; ‚Äď 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secreta ...
, Adolf Hitler
Adolf Hitler (; 20 April 188930 April 1945) was an Austrian-born German politician who was dictator of Nazi Germany, Germany from 1933 until Death of Adolf Hitler, his death in 1945. Adolf Hitler's rise to power, He rose to power as the le ...
and Joseph Stalin, once again, to return, after the end of World War II, to its original name ‚Äď Lipowa Street.
 The city covers of which is
The city covers of which is agricultural land
Agricultural land is typically land ''devoted to'' agriculture, the systematic and controlled use of other organism, forms of lifeparticularly the rearing of livestock and production of cropsto produce food for humans. It is generally synonymous ...
, is urbanized area
An urban area, built-up area or urban agglomeration is a human settlement with a high population density and infrastructure of built environment. Urban areas are created through urbanization and are categorized by urban morphology as cities, ...
s, is surface waters and is wasteland. The composition of the districts vary from residential near the city center, with a combination of multi-story apartment buildings and individual houses on small parcels, to industrial and agricultural at the city edges.
Metropolitan BiaŇāystok
Metropolitan BiaŇāystok was designated by the Voivodeship of the Regulation No. 52/05 of 16 May 2005 to help develop the region economically. In 2006, the metropolitan area population was 450,254 inhabitants. The municipalities adjacent to BiaŇāystok are slowly losing their agricultural character, becoming residential suburban neighborhoods with single-family housing and small businesses.Demographics
In June 2020, the population of the city was 296,958. Among the cities of Poland, BiaŇāystok is second in terms of population density, tenth in population, and thirteenth in area. Historically, BiaŇāystok has been a destination for internal and foreign immigration, especially fromCentral
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
. In addition to the Polish minority, there was formerly a Jewish majority in BiaŇāystok. The Jewish share in the population of BiaŇāystok grew from 22.4% (761) in 1765 to 66.6% (6,000) in 1808 and 76% (47,783) in 1895. According to the Russian census of 1897
The first general census of the population of the Russian Empire in 1897 (Russian alphabet#Letters eliminated in 1917–18, pre-reform Russian: ) was the first and only nation-wide census performed in the Russian Empire (the Grand Duchy of Fi ...
, out of the total population of 66,000, Jews
Jews ( he, ◊ô÷į◊Ē◊ē÷ľ◊ď÷ī◊ô◊Ě, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
constituted 41,900 (around 63% percent). According to the German census of 1916, Jews comprised about 72% of the inhabitants (no less than 40,000). The demographic situation changed due to the influx of Polish repatriants, intelligentsia
The intelligentsia is a status class composed of the university-educated people of a society who engage in the complex mental labours by which they critique, shape, and lead in the politics, policies, and culture of their society; as such, the in ...
and civil servants, the outflow of Jews, and the enlargement of the city after the World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. According to the 1931 census, the population of BiaŇāystok totalled 91,101: 45.5% (41,493) Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 43% (39,165) Jews (by religion), and 8.2% (7,502) Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "canonical") ...
believers.
In 1936, BiaŇāystok had a population of 99,722, of whom: 50.9% (50,758) were Poles, 42.6% (42,482) Jews, 2.1% (2,094) Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and 0.4% (359) Russians; 46.6% (45,474) adhered to the Catholic religion, 43% (42,880) to Judaism, 8.2% (8,177) to Eastern Orthodoxy and 2.9% (2,892) to Evangelicalism
Evangelicalism (), also called evangelical Christianity or evangelical Protestantism, is a worldwide interdenominational movement within Protestant Christianity that affirms the centrality of being " born again", in which an individual exper ...
. World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
changed all of this: in 1939, around 107,000 people lived in BiaŇāystok, but by 1946, the population had dropped to 56,759, with much less ethnic diversity than it had had previously. Currently the city's population is 97% Polish, 2.5% Belarusian and 0.5% of a number of minorities including Russians, Lithuanians, Ukrainians. Most of the modern-day population growth is based on internal migration within Poland and urbanization of surrounding areas.
Governance
City government
BiaŇāystok, like other major cities in Poland, is a city county ( pl, Miasto na prawach powiatu). TheLegislative power
A legislature is an assembly with the authority to make laws for a political entity such as a country or city. They are often contrasted with the executive and judicial powers of government.
Laws enacted by legislatures are usually known as p ...
in the city is vested in the unicameral
Unicameralism (from ''uni''- "one" + Latin ''camera'' "chamber") is a type of legislature, which consists of one house or assembly, that legislates and votes as one.
Unicameral legislatures exist when there is no widely perceived need for multic ...
BiaŇāystok City Council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
( pl, Rada Miasta), which has 28 members. Council members are elected directly every four years, one of whom is the mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
, or President
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966‚Äď2010 Japanese ful ...
of BiaŇāystok ( pl, prezydent). Like most legislative bodies, the City Council divides itself into committees which have the oversight of various functions of the city government. Bills passed by a simple majority are sent to the mayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
, who may sign them into law. If the mayor vetoes a bill, the Council has 30 days to override the veto by a two-thirds majority 2/3 may refer to:
* A fraction with decimal value 0.6666...
* A way to write the expression "2 √∑ 3" ("two divided by three")
* 2nd Battalion, 3rd Marines of the United States Marine Corps
* February 3
* March 2
Events Pre-1600
* 537 – ...
vote. The current President of BiaŇāystok, elected for his first term in 2006, is Tadeusz Truskolaski
Tadeusz Truskolaski (born 10 April 1958, in Stare Kapice, BiaŇāystok County, Poland) is an economist and politician. A member of the Civic Platform ''(Platforma Obywatelska)'' party, he has been the president (mayor) of the Polish city of BiaŇā ...
won the elections as the Civic Platform
Civic Platform ( pl, Platforma Obywatelska, PO)The party is officially the Civic Platform of the Republic of Poland (''Platforma Obywatelska Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''). is a political party in Poland. It is currently led by Donald Tusk.
It w ...
's candidate, however, he has no official connection with the party. In the first round of the elections he received 49% of the votes (42,889 votes altogether). In the later runoff he defeated his rival candidate Marek Kozlowski from Law and Justice
Law and Justice ( pl, Prawo i SprawiedliwoŇõńá , PiS) is a right-wing populist and national-conservative political party in Poland. Its chairman is JarosŇāaw KaczyŇĄski.
It was founded in 2001 by JarosŇāaw and Lech KaczyŇĄski as a direct su ...
( pl, Prawo i SprawiedliwoŇõńá), receiving 67% of the votes cast (53,018 votes).
For the 2010‚Äď2011 fiscal year the city received revenue (taxes levied + investments) of 1,409,565,525 zŇā, expended 1,676,459,102 zŇā leaving a budget deficit of 266,893,577 zŇā. The deficit was covered by short-term borrowing of 166,893,577 zŇā and the issuance of 100 million zŇā in municipal bond
A municipal bond, commonly known as a muni, is a Bond (finance), bond issued by state or local governments, or entities they create such as authorities and special districts. In the United States, interest income received by holders of municipal ...
s.
Other levels of governmental representationIt is also the seat of government for the
Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
. The city is represented by several members of both houses of the Polish Parliament (Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of t ...
and Senat) from the BiaŇāystok constituency. BiaŇāystok is represented by the Podlaskie and Warmian-Masurian constituency of the European Parliament
The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adopts ...
.
International relations
There are nine consulates in BiaŇāystok, aConsulate General
A consul is an official representative of the government of one state in the territory of another, normally acting to assist and protect the citizens of the consul's own country, as well as to facilitate trade and friendship between the people ...
of Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, –†–Ķ—Ā–Ņ—É–Ī–Ľ–ł–ļ–į –Ď–Ķ–Ľ–į—Ä—É—Ā—Ć, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by R ...
and Honorary Consulates of Romania
Romania ( ; ro, Rom√Ęnia ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
, Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia‚ÄďHerzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
, Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, –Ď—ä–Ľ–≥–į—Ä–ł—Ź, B«élgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon ...
, Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naŇ°a domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
, Estonia
Estonia, formally the Republic of Estonia, is a country by the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland across from Finland, to the west by the sea across from Sweden, to the south by Latvia, a ...
, Luxembourg
Luxembourg ( ; lb, L√ętzebuerg ; french: link=no, Luxembourg; german: link=no, Luxemburg), officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg, ; french: link=no, Grand-Duch√© de Luxembourg ; german: link=no, Gro√üherzogtum Luxemburg is a small lan ...
and Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
. The City of BiaŇāystok is a member of several organizations such as Union of Polish Metropolises ( pl, Unia Metropolii Polskich), Euroregion Niemen, Polish Green Lungs Foundation, and Eurocities
Eurocities is a network of large cities in Europe, established in 1986 by the mayors of six large cities: Barcelona, Birmingham, Frankfurt, Lyon, Milan and Rotterdam. Today, Eurocities members includes over 200 of Europe's major cities from 38 c ...
.
BiaŇāystok is twinned with:
* Eindhoven
Eindhoven () is a city and municipality in the Netherlands, located in the southern province of North Brabant of which it is its largest. With a population of 238,326 on 1 January 2022,Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Trakai ...
, Lithuania
* Milwaukee
Milwaukee ( ), officially the City of Milwaukee, is both the most populous and most densely populated city in the U.S. state of Wisconsin and the county seat of Milwaukee County. With a population of 577,222 at the 2020 census, Milwaukee is ...
, United States
* Dijon
Dijon (, , ) (dated)
* it, Digione
* la, DiviŇć or
* lmo, Digion is the prefecture of the C√īte-d'Or department and of the Bourgogne-Franche-Comt√© region in northeastern France. the commune had a population of 156,920.
The earlies ...
, France
* Yehud
Yehud ( he, ◊ô÷į◊Ē◊ē÷ľ◊ď) is a city in the Central District (Israel), Central District of Israel that is part of the joint municipality of Yehud-Monosson. In 2007, the city's population stood at approximately 30,000 people (including Neve Monosson ...
, Israel
* Jelgava
Jelgava (; german: Mitau, ; see also other names) is a state city in central Latvia about southwest of Riga with 55,972 inhabitants (2019). It is the largest town in the region of Zemgale (Semigalia). Jelgava was the capital of the united Duch ...
, Latvia
* Mazara del Vallo
Mazara del Vallo (; ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Trapani, southwestern Sicily, Italy. It lies mainly on the left bank at the mouth of the Mazaro river.
It is an agricultural and fishing centre and its port gives shelter to the ...
, Italy
* Lusaka
Lusaka (; ) is the Capital city, capital and largest city of Zambia. It is one of the fastest-developing cities in southern Africa. Lusaka is in the southern part of the central plateau at an elevation of about . , the city's population was ab ...
, Zambia
* Bornova
Bornova is a metropolitan district of ńįzmir in ńįzmir Province in Turkey. It is the third largest district in ńįzmir's Greater Metropolitan Area of and is almost fully urbanized at the rate of 98.6 percent, with corresponding high levels of devel ...
, Turkey
* Chongzuo
Chongzuo (; za, Cungzcoj) is a prefecture-level city in the south of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region near the Sino-Vietnamese border. It is home to one of China's largest Zhuang populations.
Geography and climate
Chongzuo is located in sout ...
, China
* Sliema
Sliema ( mt, Tas-Sliema ) is a town located on the northeast coast of Malta in the Districts of Malta#Northern Harbour District, Northern Harbour District. It is a major residential and commercial area and a centre for shopping, bars, dining, a ...
, Malta
* Dobrich
Dobrich ( bg, –Ē–ĺ–Ī—Ä–ł—á ; ro, Bazargic, tr, HacńĪońülu PazarcńĪk) is the List of cities and towns in Bulgaria, 9th most populated city in Bulgaria, the administrative centre of Dobrich Province and the capital of the region of Southern Dobr ...
, Bulgaria
* Bahir Dar
Bahir Dar ( amh, ŠČ£ŠąēŠą≠ Šč≥Šą≠, 3=sea shore) is the capital city of Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Bahir Dar is one of the leading tourist destinations in Ethiopia, with a variety of attractions in the nearby Lake Tana and Blue Nile river. The ci ...
, Ethiopia
Former twin towns:
* Irkutsk
Irkutsk ( ; rus, –ė—Ä–ļ—É—ā—Ā–ļ, p=…™rňąkutsk; Buryat language, Buryat and mn, –≠—Ä—Ö“Į“Į, ''Erh√ľ√ľ'', ) is the largest city and administrative center of Irkutsk Oblast, Russia. With a population of 617,473 as of the 2010 Census, Irkutsk is ...
, Russia
* Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, –ö–į–Ľ–ł–Ĺ–ł–Ĺ–≥—Ä–į–ī, p=k…ôl ≤…™n ≤…™nňą…°rat, links=y), until 1946 known as K√∂nigsberg (; rus, –ö—Ď–Ĺ–ł–≥—Ā–Ī–Ķ—Ä–≥, Kyonigsberg, ňąk ≤…Ķn ≤…™…°zb…õrk; rus, –ö–ĺ—Ä–ĺ–Ľ–ĶŐĀ–≤–Ķ—Ü, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
, Russia
* Pskov
Pskov ( rus, –ü—Ā–ļ–ĺ–≤, a=pskov-ru.ogg, p=pskof; see also names in other languages) is a city in northwestern Russia and the administrative center of Pskov Oblast, located about east of the Estonian border, on the Velikaya River. Population ...
, Russia
* Tomsk
Tomsk ( rus, –Ę–ĺ–ľ—Ā–ļ, p=tomsk, sty, –Ę“Į“£-—ā–ĺ—Ä–į) is a city and the administrative center of Tomsk Oblast in Russia, located on the Tom River. Population:
Founded in 1604, Tomsk is one of the oldest cities in Siberia. The city is a not ...
, Russia
On 3 March 2022, BiaŇāystok ended its partnership with the Russian cities of Irkutsk, Kaliningrad, Pskov and Tomsk, and also with the Belarusian city of Grodno as a reaction to the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. An ...
.
Eastern Partnership
The Eastern Partnership (EaP) is a joint initiative of the European External Action Service of the European Union (EU) together with the EU, its member states, and six Eastern European partners governing the EU's relationship with the post-Sovi ...
cities:
* Lutsk
Lutsk ( uk, –õ—É—Ü—Ć–ļ, translit=Lutsk}, ; pl, ŇĀuck ; yi, ◊ú◊ē◊¶◊ß, Lutzk) is a city on the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Volyn Oblast (province) and the administrative center of the surrounding Luts ...
, Ukraine
* Gori, Georgia
* BńÉl»õi
BńÉl»õi (; russian: –Ď–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Ü—č, , uk, –Ď—Ē–Ľ—Ć—Ü—Ė, , yi, ◊Ď◊Ę◊ú◊• ) is a city in Moldova. It is the second largest city in terms of population, area and economic importance, after Chi»ôinńÉu. The city is one of the five Moldovan municipalit ...
, Moldova
* Gyumri
Gyumri ( hy, ‘≥’Ķ’ł÷ā’ī÷Ä’ę, ) is an urban municipal community and the second-largest city in Armenia, serving as the administrative center of Shirak Province in the northwestern part of the country. By the end of the 19th century, when the city w ...
, Armenia
* Sumgait
Sumgait (; az, SumqayńĪt, ) is a city in Azerbaijan, located near the Caspian Sea, on the Absheron Peninsula, about away from the capital Baku. The city has a population of around 345,300, making it the second largest city in Azerbaijan after Bak ...
, Azerbaijan
Former partnership:
* Grodno
Grodno (russian: –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–ĺ, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–į ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
, Belarus
Military units
The construction of theSaint Petersburg‚ÄďWarsaw Railway
Saint Petersburg‚ÄďWarsaw Railway (() (transliteration: Sankt-Peterburgo‚ÄďVarshavskaya zheleznaya doroga)) is a long railway, built in the 19th century by the Russian Empire to connect Russia with Central Europe. At the time the entire railwa ...
which passed through the city and was the strategic nerve of the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, resulted in the rising of the military importance of the city: In 1879, construction of the barracks of the WŇāodzimierski Infantry Regiment began (currently it is the area of the Voivodeship hospital between Wojskowa, SkŇāodowskiej-Curie and WoŇāodyjowskiego Streets). In 1884, barracks of the Kazan Infantry Regiment were established at Traugutta Street in Wygoda. In 1887, barracks of the Mariampole Dragon Regiment were erected at 100 Bema Street. In 1890, the barracks of Kharkov Uhlans Regiment were built at Kawaleryjska Street.
Throughout the interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the World War I, First World War to the beginning of the World War II, Second World War. The in ...
and the existence of the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central Europe, Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 1918 and 1939. The state was established on 6 November 1918, before the end of ...
, the city enjoyed the presence of the 42nd Infantry Regiment (barracks at Wygoda), 10th Lithuanian Uhlan Regiment (Kawaleryjska Street) and the 14th Horse Artillery Squadron ( pl, 14 Dywizjon Artylerii Konnej) (Bema Street), the command of the Podlaska Cavalry Brigade The Podlaska Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ''Podlaska Brygada Kawalerii'') was a military unit of the Polish Army, created on April 1, 1937. Its headquarters were in BiaŇāystok, and it was based on the ''Cavalry Brigade BiaŇāystok'', existing between Feb ...
and spare center (Skladowej-Curie Street, then Piwna), units of the Armed Forces of the Second Polish Republic.
Polish Land Forces
The Land Forces () are the land forces of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000 active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stret ...
is based in BiaŇāystok. The heritage of the unit was the former 18th Territorial Defense Battalion ( pl, 18 BiaŇāostocka Brygada Obrony Terytorialnej) and prior to that the former 18th Mechanized Brigade. December 31, 2001, as a result of the restructuring of the Armed Forces, 18th Mechanized Brigade ( pl, 18 Brygada Zmechanizowana) was disbanded and in its place created the 18th Territorial Defense Battalion ( pl, 18 BiaŇāostocka Brygada Obrony Terytorialnej).
The Cavalry Brigade "BiaŇāystok" (BK "BiaŇāystok") of the Polish Army Second Republic was formed in February 1929. On April 1, 1937, BK "BiaŇāystok" was renamed the Podlaska Cavalry Brigade The Podlaska Cavalry Brigade (Polish: ''Podlaska Brygada Kawalerii'') was a military unit of the Polish Army, created on April 1, 1937. Its headquarters were in BiaŇāystok, and it was based on the ''Cavalry Brigade BiaŇāystok'', existing between Feb ...
( pl, Podlaska Brygada Kawalerii). Its headquarters was located in BiaŇāystok and operated as part of Independent Operational Group Narew
Independent Operational Group Narew (''Samodzielna Grupa Operacyjna Narew'', SGO Narew) was one of the Polish Army Corps (Operational Groups) that defended Poland during the Invasion of Poland in 1939. It was created on 23 March 1939 and was com ...
. It was formed from the Cavalry Brigade "BiaŇāystok", which existed between February 1929, and March 30, 1937. After the Soviet invasion of Poland
The Soviet invasion of Poland was a military operation by the Soviet Union without a formal declaration of war. On 17 September 1939, the Soviet Union invaded Poland from the east, 16 days after Nazi Germany invaded Poland from the west. Subse ...
, remnants of the Brigade fought both Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the ''Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previous ...
and Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian: –†–į–Ī–ĺŐĀ—á–Ķ-–ļ—Ä–Ķ—Ā—ā—Ć—ŹŐĀ–Ĺ—Ā–ļ–į—Ź –ö—Ä–įŐĀ—Ā–Ĺ–į—Ź –į—Ä–ľ–ł—Ź),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic and, after ...
troops, capitulating on October 6, 1939.
During December 1993 an order of the Chief of the General Staff of the Polish Armed Forces created the 18th Mechanized Brigade ( pl, 18 Brygada Zmechanizowana) at the garrison in BiaŇāystok. The unit was formed from the 3rd Mechanized Regiment ( pl, 3 PuŇāk Zmechanizowany) and was subordinated to the commander of the 1st Warsaw Mechanized Division ( pl, 1 Warszawskiej Dywizji Zmechanizowanej im. Tadeusza KoŇõciuszki). On December 31, 2001, as a result of the restructuring of the Armed Forces, the 18th Mechanized Brigade was disbanded and in its place was created the 18th Territorial Defense Battalion.
Economy
 In the nineteenth century, BiaŇāystok was an important center for light industry, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The tradition continued with many garment factories established in the twentieth century, such as ''Fasty'' in the district of Bacieczki. However, after the fall of communism in 1989 many of these factories faced severe problems and subsequently closed down.
The unemployment rate for November 2020 in BiaŇāystok was 6.8%.
The 2009 average household had a monthly per capita income of 1018.77 zŇā and monthly per capita expenses of 823.56 zŇā
The city has a number of nearby border crossings. The border with Belarus is only away, the nearest border crossings are located in;
In the nineteenth century, BiaŇāystok was an important center for light industry, which was the reason for the substantial growth of the city's population. The tradition continued with many garment factories established in the twentieth century, such as ''Fasty'' in the district of Bacieczki. However, after the fall of communism in 1989 many of these factories faced severe problems and subsequently closed down.
The unemployment rate for November 2020 in BiaŇāystok was 6.8%.
The 2009 average household had a monthly per capita income of 1018.77 zŇā and monthly per capita expenses of 823.56 zŇā
The city has a number of nearby border crossings. The border with Belarus is only away, the nearest border crossings are located in; Bobrowniki
Bobrowniki (; german: Beberen) is a village in Lipno County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Bobrowniki. It lies approximately south-west of Lipno an ...
(road crossing located about from the city limits), KuŇļnica BiaŇāostocka KuŇļnica is a Polish toponym meaning ''Hammer mill'', it may refer to:
*KuŇļnica, Pomeranian Voivodeship (north Poland), a district of the seaside town of Jastarnia
:* KuŇļnica railway station
* KuŇļnica, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship (north-cent ...
(road and rail crossing located from the city limits), Siemian√≥wka (railway ‚Äď freight traffic), PoŇāowce
PoŇāowce is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Czeremcha, within Hajn√≥wka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It lies approximately south of Czeremcha, south-west of Hajn√≥wka ...
(road) and Czeremcha
Czeremcha ( uk, –ß–Ķ—Ä–Ķ–ľ—Ö–į, ''Cheremkha'') is a village in Hajn√≥wka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Czeremcha. It lies app ...
(railway). Since the border with Belarus is also the eastern border of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
, as well as the Schengen Area
The Schengen Area ( , ) is an area comprising 27 European countries that have officially abolished all passport and all other types of border control at their mutual borders. Being an element within the wider area of freedom, security and j ...
the city is a center for trade in mainly from the east.

 The leading industries in the city's economy are food processing (production of meat products, fruit and vegetable products, the production of
The leading industries in the city's economy are food processing (production of meat products, fruit and vegetable products, the production of spirits
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
, the production of frozen food, grain processing), electrical engineering (production tools and equipment for machine tools, production of electric heaters, manufacture and production mixers household appliances). There is also a developed machine industry (electronics, machinery and metal), plastic processing (production of household appliances), textiles (textiles and upholstery, manufacture of underwear, clothing accessories, footwear and backpacks), Wood (production plywood and furniture) building materials.
Some major employers who are based in BiaŇāystok include:
* ''Dojlidy Brewery
Dojlidy Brewery ( pl, Browar Dojlidy ) is a brewery located in BiaŇāystok, Poland, and owned by Kompania Piwowarska SA, the Polish subsidiary of Asahi Breweries. The brewery was modernized between 1997 and 1999, then in 2003 it was purchased b ...
'' in the district of Dojlidy produces the second most popular beer
Beer is one of the oldest and the most widely consumed type of alcoholic drink in the world, and the third most popular drink overall after water and tea. It is produced by the brewing and fermentation of starches, mainly derived from ce ...
in Poland, '' ŇĽubr''.
* ''Polmos BiaŇāystok
Polmos BiaŇāystok is one of the largest producers of alcoholic beverages in Poland. As of 2010, the firm's president was Henryk Wnorowski. Between 2005 and 2007 the company's stock was traded on the Warsaw Stock Exchange.
The firm was founded ...
'', the biggest vodka
Vodka ( pl, w√≥dka , russian: –≤–ĺ–ī–ļ–į , sv, vodka ) is a clear distilled alcoholic beverage. Different varieties originated in Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Vodka is composed mainly of water and ethanol but sometimes with traces of impuritie ...
manufacturer in Poland, is located in the city district of Starosielce. The company produces ''Absolwent
Absolwent is a Polish luxury vodka manufactured since 1995 by Polmos BiaŇāystok. Produced as a 4-fold rectified grain high-end spirit.
It occurs in several varieties: pure, flavor (such as lemon, apricot, cranberry
Cranberries are a gr ...
'' and ''ŇĽubr√≥wka
ŇĽubr√≥wka Bison Grass Vodka () is a flavored Polish vodka, which contains a bison grass blade (''Hierochloe odorata'') in every bottle. The ŇĽubr√≥wka brand name is also used on bottles of conventional vodka, labeled as ŇĽubr√≥wka BiaŇāa. An eas ...
'' (bison grass vodka) ‚Äď both major exports abroad.
* ''Standard Motor Products Poland Ltd.'' headquartered in BiaŇāystok began manufacturing ignition coils for original equipment manufacturers 30 years ago.
* ''"Supon" BiaŇāystok'' is the leading Polish producer of fire fighting equipment.
* ''SavaPol, Sp.z o.o.'' is a manufacturer of stationary and mobile concrete mixing equipment based in BiaŇāystok.
* ''Biazet S.A.'' is a large manufacture of household appliances, including vacuum cleaners, coffee makers, and LED lighting located in BiaŇāystok.
* ''Agnella'', a major Polish producer of carpets and similar products is in BiaŇāystok, located in the district of BiaŇāostoczek.
* ''Rosti Poland Sp. z o.o.'', has provided for more than 60 years precision injection molded products for some of the world's leading brands.
* ''Biaglass Huta Szkla BiaŇāystok Sp. z o.o.'', established in 1929, produces mouth blown glass lampshades and related products. Biaglass belongs to elite group of Glass Works in Europe, where 100% of the lighting glass is mouth-blown.
* ''ChŇāodnia BiaŇāystok S.A'' (Cold Store BiaŇāystok S.A.), established in 1952, is one of the largest Polish producers of frozen vegetables, fruits and ready-to-heat meals.
* ''Podlaskie ZakŇāady ZboŇľowe S.A.'' was established on 1 July 2000 as a result of privatizing The Regional Establishment of Corn and Milling Industry 'PZZ' in BiaŇāystok. It is one of the leading firms in Podlaskie region in the department of preservation and processing of grain with elevators in BiaŇāystok, Grajewo
Grajewo (, yi, ◊í◊®◊ź◊ô◊Ę◊ē◊ē◊Ę, translit=Grayavah) is a town in north-eastern Poland with 21,499 inhabitants (2016). It is situated in the Podlaskie Voivodeship (since 1999); previously, it was in ŇĀomŇľa Voivodeship (1975‚Äď1998). It is the ...
and SuwaŇāki
SuwaŇāki ( lt, Suvalkai; yi, ◊°◊ē◊ź◊ē◊ē◊ź÷∑◊ú◊ß) is a city in northeastern Poland with a population of 69,206 (2021). It is the capital of SuwaŇāki County and one of the most important centers of commerce in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. SuwaŇāki i ...
.
Culture and tourism
 BiaŇāystok is one of the largest cultural centers in the
BiaŇāystok is one of the largest cultural centers in the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
. The attractions include performing arts groups, art museums, historical museums, walking tours of architectural/cultural aspects and a wide variety of parks and green spaces. BiaŇāystok in 2010 was on the short-list, but ultimately lost the competition, to become a finalist for European Capital of Culture in 2016.
Performing arts
The city has a number of performing arts facilities including: TheBiaŇāystok Puppet Theatre
Bialystok Puppet Theatre ( pl, BiaŇāostocki Teatr Lalek), founded in 1953, is one of the oldest puppet theaters in Poland. Its repertoire consists mainly of puppetry-based adaptations of international literature, as well as children's entertainme ...
( pl, Bialostocki Teatr Lalek), established in 1953, is one of the oldest Polish puppet theater
A puppet is an object, often resembling a human, animal or mythical figure, that is animated or manipulated by a person called a puppeteer. The puppeteer uses movements of their hands, arms, or control devices such as rods or strings to mov ...
s. The facility is located at Kalinowskiego 1 in BiaŇāystok. The repertoire includes performances for both children and puppet adaptations of world literature for adults. Because of the high artistic level of productions, the theater has been recognized as one of the best puppetry arts centers in Poland.
The Aleksandra Wńôgierki Drama Theatre, housed in a building designed by JarosŇāaw Girina, was built in the years 1933‚Äď1938.
The Podlasie Opera and Philharmonic ‚Äď European Art Centre in BiaŇāystok is the largest institute of arts in Northeastern Poland and the most modern cultural center in this region of Europe. In its amphitheatre every year at the end of June Halfway Festival
Halfway Festival is a music festival which takes place in Northeastern Poland, in BiaŇāystok in the last week of June every year. The festival's main organizer is the Podlasie Opera and Philharmonic ‚Äď European Art Centre. Its first edition ...
takes place.
Museums
 There are a number of museums in the city including:
The Historical Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Historyczne w BiaŇāymstoku) is part of the Podlaskie Museum. The facility has a rich collection of archival materials and
There are a number of museums in the city including:
The Historical Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Historyczne w BiaŇāymstoku) is part of the Podlaskie Museum. The facility has a rich collection of archival materials and iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
illustrating the history of BiaŇāystok and Podlasie
Podlachia, or Podlasie, ( pl, Podlasie, , be, –ü–į–ī–Ľ—Ź—ą—ą–į, translit=PadliaŇ°Ň°a, uk, –ü—Ė–ī–Ľ—Ź—ą—ą—Ź, translit=Pidliashshia) is a historical region in the north-eastern part of Poland. Between 1513 and 1795 it was a voivodeship with the c ...
, and a number of middle-class cultural relics, especially in the field of craft utility. There are also the Numismatic Cabinet of the collection of 16 000 coins, medals and securities. The museum is in possession of the only collections in the country memorabilia connected with the Tatar settlement on the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian‚ÄďBelarusian region.
 The Army Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Wojska w BiaŇāymstoku) was established in September 1968 as a branch of the Podlaskie Museum to house the research and collections of many people connected with the military history of north-eastern Poland.
The Army Museum in BiaŇāystok ( pl, Muzeum Wojska w BiaŇāymstoku) was established in September 1968 as a branch of the Podlaskie Museum to house the research and collections of many people connected with the military history of north-eastern Poland.
The Ludwik Zamenhof Centre
The Ludwik Zamenhof Centre is a cultural institution located in BiaŇāystok, Poland, at ''ulica Warszawska 19'' (!9 Warsaw Street). It was founded at the initiative of the city's president (mayor) in celebration of the 94th World Congress of Espera ...
( pl, Centrum im. Ludwika Zamenhofa w BiaŇāymstoku) has a permanent exhibition, "Bialystok of Young Ludwik Zamenhof
L. L. Zamenhof (15 December 185914 April 1917) was an ophthalmologist who lived for most of his life in Warsaw. He is best known as the creator of Esperanto, the most widely used constructed language, constructed international auxiliary language ...
", and various temporary exhibitions, concerts, film projections, and theatre performances. The Centre has a branch of Lukasz Gornicki's Podlaska Library dedicated to the Esperanto
Esperanto ( or ) is the world's most widely spoken constructed international auxiliary language. Created by the Warsaw-based ophthalmologist L. L. Zamenhof in 1887, it was intended to be a universal second language for international communi ...
language.
 The Sybir Memorial Museum ( pl, Muzeum Pamińôci Sybiru) is a historical museum opened in 2021 and dedicated to the memory of Poles as well as people from other nationalities who were the victims of forced deportations to
The Sybir Memorial Museum ( pl, Muzeum Pamińôci Sybiru) is a historical museum opened in 2021 and dedicated to the memory of Poles as well as people from other nationalities who were the victims of forced deportations to Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, –°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć, r=Sibir', p=s ≤…™ňąb ≤ir ≤, a=Ru-–°–ł–Ī–ł—Ä—Ć.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
perpetrated by Russia and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national ...
.
Parks and green spaces
 Around 32% of the city is occupied by parks, squares and forest preserves which creates a unique and healthy climate. The green spaces include:
Branicki Palace ( pl, PaŇāac Branickich) is a historical edifice and park in BiaŇāystok. It was developed on the site of an earlier building in the first half of the eighteenth century by
Around 32% of the city is occupied by parks, squares and forest preserves which creates a unique and healthy climate. The green spaces include:
Branicki Palace ( pl, PaŇāac Branickich) is a historical edifice and park in BiaŇāystok. It was developed on the site of an earlier building in the first half of the eighteenth century by Jan Klemens Branicki
Count Jan Klemens Branicki (also known as Jan Kazimierz Branicki; 21 September 1689 ‚Äď 9 October 1771) was a Polish nobleman, magnate and Hetman, Field Crown Hetman of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth between 1735 and 1752, and Great Crown ...
, a wealthy Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
hetman
( uk, –≥–Ķ—ā—Ć–ľ–į–Ĺ, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military co ...
, into a residence
A residence is a place (normally a building) used as a home or dwelling, where people reside.
Residence may more specifically refer to:
* Domicile (law), a legal term for residence
* Habitual residence, a civil law term dealing with the status ...
suitable for a man whose ambition was to be elected king of Poland. The palace complex with gardens
A garden is a planned space, usually outdoors, set aside for the cultivation, display, and enjoyment of plants and other forms of nature. The single feature identifying even the wildest wild garden is ''control''. The garden can incorporate both ...
, pavillons, sculptures
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
, outbuildings and other structures and the city with churches, city hall
In local government, a city hall, town hall, civic centre (in the UK or Australia), guildhall, or a municipal building (in the Philippines), is the chief administrative building of a city, town, or other municipality. It usually houses ...
and monastery
A monastery is a building or complex of buildings comprising the domestic quarters and workplaces of monastics, monks or nuns, whether living in communities or alone (hermits). A monastery generally includes a place reserved for prayer which ...
, all built almost at the same time according to French models was the reason why the city was known in the eighteenth century as Versailles
The Palace of Versailles ( ; french: Ch√Ęteau de Versailles ) is a former royal residence built by King Louis XIV located in Versailles, about west of Paris, France. The palace is owned by the French Republic and since 1995 has been managed, u ...
of Podlaskie
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
( pl, wersalem podlaskim).
Planty is a park created between 1930 and 1938, under the auspices of the then voivode Marian Zyndram-KoŇõciaŇākowski
Marian Zyndram-KoŇõciaŇākowski (; 16 March 1892, Pandńólys, Kovno Governorate ‚Äď 12 April 1946 Brookwood, Surrey) was a Polish politician, freemason and military officer who served as voivode of BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1919-1939), BiaŇāystok Voi ...
in the areas adjacent to Branicki Palace. The modernist composition of the park was designed by Stanislav Gralla.
Architecture
 The various historically driven changes have had a very significant influence on the architectural space of the city. Most other Polish cities have suffered similarly, but the processes in BiaŇāystok, have had a particularly intense course. Numerous historic works of architecture no longer exist, while many others have been rebuilt to their original configuration. Very few historic buildings of the city have been preserved ‚Äď the sights are merely an echo of the old historical shape of BiaŇāystok.
Main sights include:
* Palaces: Branicki Palace, Branicki Guest Palace, Lubomirski Palace, Hasbach Palace, Nowik Palace
* Townhall
* Catholic Cathedral
* St. Roch Church
* St. Adalbert Church
* Orthodox Cathedral
* Daughters of Charity Monastery
* Former Arsenal
* Former Masonic Lodge
The various historically driven changes have had a very significant influence on the architectural space of the city. Most other Polish cities have suffered similarly, but the processes in BiaŇāystok, have had a particularly intense course. Numerous historic works of architecture no longer exist, while many others have been rebuilt to their original configuration. Very few historic buildings of the city have been preserved ‚Äď the sights are merely an echo of the old historical shape of BiaŇāystok.
Main sights include:
* Palaces: Branicki Palace, Branicki Guest Palace, Lubomirski Palace, Hasbach Palace, Nowik Palace
* Townhall
* Catholic Cathedral
* St. Roch Church
* St. Adalbert Church
* Orthodox Cathedral
* Daughters of Charity Monastery
* Former Arsenal
* Former Masonic Lodge
Sports
The city has both professional and amateur sports teams, and a number of venues where they are based.Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok
Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok () is a Polish football club based in BiaŇāystok that plays in the Ekstraklasa, the top level of Polish football. The club was founded in 1920 by soldiers in the Reserve Battalion in BiaŇāystok. Jagiellonia play their home g ...
is a Polish football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
club, based in BiaŇāystok, in the Ekstraklasa
Poland Ekstraklasa (), meaning "Extra Class" in Polish, named PKO Ekstraklasa since the 2019‚Äď20 season due to its sponsorship by PKO Bank Polski, is the top Polish professional league for men's association football teams.
Contested by 18 cl ...
(Poland's top division) that plays at the BiaŇāystok City Stadium
BiaŇāystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
BiaŇāystok is located in the BiaŇāystok U ...
. Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok
Jagiellonia BiaŇāystok () is a Polish football club based in BiaŇāystok that plays in the Ekstraklasa, the top level of Polish football. The club was founded in 1920 by soldiers in the Reserve Battalion in BiaŇāystok. Jagiellonia play their home g ...
won the Polish Cup in 2010, Super Cup and qualified to play in the third round qualification of the UEFA Europa League
The UEFA Europa League (abbreviated as UEL, or sometimes, UEFA EL), formerly the UEFA Cup, is an annual football club competition organised since 1971 by the Union of European Football Associations (UEFA) for eligible European football clubs. It ...
. A new 22,500-seat stadium was completed at the beginning of 2015.
Hetman BiaŇāystok (formerly known as Gwardia BiaŇāystok) is a Polish football club based in Podlaskie Voivodeship. They play in the Division IV or the (4th) League.
Lowlanders BiaŇāystok
The Lowlanders BiaŇāystok is an American football team based in BiaŇāystok, Poland. They play in the Polish Football League.
History
The team joined to the PLFA II in 2008 PLFA season. Lowlanders won the PLFA II and was promoted to the PLFA I. ...
is a football
Football is a family of team sports that involve, to varying degrees, kicking a ball to score a goal. Unqualified, the word ''football'' normally means the form of football that is the most popular where the word is used. Sports commonly c ...
club, based in BiaŇāystok, that plays in the Polish American Football League
The Polish American Football League or shortly PLFA ( pl, Polska Liga Futbolu AmerykaŇĄskiego) was a structured system for the American football competitions in Poland founded in 2004 by the Polish federation PZFA. In 2012, the Topliga was creat ...
( pl, Polska Liga Futbolu AmerykaŇĄskiego) PLFA I Conference. The Lowlanders were the champions of the PLFA II Conference in 2010 with a perfect season (8 wins in eight meetings). Because of the win, they were advanced to the upper conference (PLFA I) in 2011.
Media
 BiaŇāystok has a wide variety of media outlets serving the city and surrounding region. There are two locally published daily newspapers,
BiaŇāystok has a wide variety of media outlets serving the city and surrounding region. There are two locally published daily newspapers, Gazeta Wsp√≥Ňāczesna
Gazeta Wsp√≥Ňāczesna is a daily newspaper in the city of BiaŇāystok, Poland. It is also a daily newspaper in the Podlasie region. The English translation is "The Modern Newspaper". There are two other newspapers in the city of BiaŇāystok and they ...
(36.3% market share) and Kurier Poranny Kurier Poranny (Polish for ''Morning Courier'') can refer to one of the following Polish newspapers:
*Kurier Poranny (1877-1939)
''Kurier Poranny'' ("Morning Courier") is a daily newspaper in BiaŇāystok and the Podlasie region of Poland
Pol ...
(20.3% market share). In addition two national papers have local bureaus. There are a number of national and locally produced television and radio channels available both over-the-air from the nearby RTCN BiaŇāystok (Krynice) Mast, the seventh highest structure in Poland, in addition to transmitter sites within the city. TVP BiaŇāystok is one of the locally produced, regional branches of the TVP, Poland's public television broadcaster. There is also a cable television system available within the city. The city has two campus radio
Campus radio (also known as college radio, university radio or student radio) is a type of radio station that is run by the students of a college, university or other educational institution. Programming may be exclusively created or produce ...
stations; ''RadiosupeŇā'' at the Medical University of BiaŇāystok
The Medical University of BiaŇāystok (UMB; Polish: ''Uniwersytet Medyczny w BiaŇāymstoku'') is a medical university located in BiaŇāystok, the capital of Podlaskie Voivodeship in northeastern Poland.
The university is home to the Medical Depart ...
and ''Radio Akadera'' at BiaŇāystok Technical University
Bialystok University of Technology ( pl, Politechnika BiaŇāostocka) is the largest technical university in northeast Poland.Roman Catholic Archdiocese of BiaŇāystok
The Archdiocese of BiaŇāystok ( la, Bialostocen(sis)) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or archdiocese of the Catholic Church in Podlaskie Voivodeship, Northeastern Poland. It is a metropolitan see with two suffragan dioceses.
Its ca ...
. Pope John Paul II on 5 June 1991, during a visit to BiaŇāystok, announced the establishment of the Archdiocese of BiaŇāystok
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
which ended the period of the temporary church administration of the portion of the Archdiocese of Vilnius
The Roman Catholic Metropolitan Archdiocese of Vilnius ( la, Archidioecesis Vilnensis; lt, Vilniaus arkivyskupija) is an ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Roman Catholic Church in Lithuania. Established as the Diocese of Vilnius in t ...
that had, after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries‚ÄĒincluding all of the great powers‚ÄĒforming two opposin ...
, remained within the Polish borders. The city is also the seat of the BiaŇāystok-Gdansk Diocese of the Autocephalous
Autocephaly (; from el, őĪŠĹźŌĄőŅőļőĶŌÜőĪőĽőĮőĪ, meaning "property of being self-headed") is the status of a hierarchical Christian church whose head bishop does not report to any higher-ranking bishop. The term is primarily used in Eastern Ort ...
Polish Orthodox Church
The Polish Autocephalous Orthodox Church ( pl, Polski Autokefaliczny KoŇõci√≥Ňā PrawosŇāawny), commonly known as the Polish Orthodox Church, or Orthodox Church of Poland, is one of the autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches in full communion. Th ...
. BiaŇāystok is the largest concentration of Orthodox believers in Poland. In BiaŇāystok, the following Protestant churches exist: a Lutheran parish, two Pentecostal churches, Baptist church, a congregation of the Church of God in Christ and a Seventh Day Adventist church.
BiaŇāystok is home to more than two thousand Muslims (mainly Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
). There is an Islamic Centre, a House of Prayer, and various organisations. There is a magazine issued ‚Äď "" ("Memory and persistence").
The city is the site of the Divine Mercy Sanctuary with the main relics of in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
MichaŇā Sopońáko
Michael Sopońáko ( pl, MichaŇā Sopońáko ; 1 November 1888 ‚Äď 15 February 1975) was a Polish Roman Catholic priest and professor at Vilnius University. He is best known as the spiritual director of Faustina Kowalska. He was beatified by Pope Bene ...
.
Orthodox Church
Orthodox Church may refer to:
* Eastern Orthodox Church
* Oriental Orthodox Churches
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church of New Zealand
* State church of the Roman Empire
* True Orthodox church
See also
* Orthodox (dis ...
of the Holy Spirit
File:BiaŇāystok, ul. Lipowa, cerkiew p. w. Ňõw. MikoŇāaja, 1846 02.JPG, Eastern Orthodox Church of St. Nicholas in Lipowa Street
Transport
 The city is and has been for centuries, the main hub of transportation for the
The city is and has been for centuries, the main hub of transportation for the Podlaskie Voivodeship
Podlaskie Voivodeship or Podlasie Province ( pl, Województwo podlaskie, ) is a voivodeship (province) in northeastern Poland. The name of the province and its territory correspond to the historic region of Podlachia. The capital and largest cit ...
and the entire northeastern section of Poland. It is a major city on the European Union roadways (Via Baltica
European route E 67 is an E-road running from Prague in the Czech Republic to Estonia and by ferry to Finland. It goes via Prague, WrocŇāaw, Warsaw, Kaunas, PanevńóŇĺys, Riga, Tallinn, Helsinki.
The route is known as the Via Baltica ...
) and railways (Rail Baltica
Rail Baltica (also known as Rail Baltic in Estonia) is a high-speed railway under construction between Warsaw, Poland and Tallinn, Estonia, with further connections to Finland via Baltic Sea cruiseferries or the proposed Helsinki‚ÄďTallinn Tunne ...
) to the Baltic Republics and Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
. It is also a main gateway of trade with Belarus due to its proximity to the border and its current and longstanding relationship with Hrodna
Grodno (russian: –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–ĺ, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–į ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
, Belarus.
A traffic management system has been operating in BiaŇāystok since 2015. At 120 intersections, traffic lights are coordinated in such a way that cars and buses covered the route as quickly as possible. Special cameras record traffic, travel time. Drivers receive this information on 19 boards set among others at the intersections on Wasilkowska Street, Antoniuk-Fabryczny Street and Kleeberga Street.Patrycja Pi√≥rkowska. Komunikacja miejska jako element systemu transportowego miasta BiaŇāystok ‚Äď wyniki badaŇĄ, p. 110
Railways
Passenger trains connect fromSuwaŇāki
SuwaŇāki ( lt, Suvalkai; yi, ◊°◊ē◊ź◊ē◊ē◊ź÷∑◊ú◊ß) is a city in northeastern Poland with a population of 69,206 (2021). It is the capital of SuwaŇāki County and one of the most important centers of commerce in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. SuwaŇāki i ...
, Grodno
Grodno (russian: –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–ĺ, pl, Grodno; lt, Gardinas) or Hrodna ( be, –ď—Ä–ĺ–ī–Ĺ–į ), is a city in western Belarus. The city is located on the Neman River, 300 km (186 mi) from Minsk, about 15 km (9 mi) from the Polish b ...
and Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
to Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
and the rest of the European passenger network. Passenger services are provided by two rail service providers, PKP Intercity
PKP Intercity is a company of PKP Group responsible for long-distance passenger transport. It runs about 350 trains daily, connecting mainly large agglomerations and smaller towns in Poland. The company also provides most international trains to ...
that provides intercity passengers trains (express, intercity, eurocity, hotel and TLK) and Przewozy Regionalne
Polregio (formerly ''Przewozy Regionalne'') is a train operator in Poland, responsible for local and interregional passenger transportation. Each day it runs approximately 3,000 regional trains. In 2002 it carried 215 million passengers.
The ...
that operates only regional passenger trains financed by the voivodeship
A voivodeship is the area administered by a voivode (Governor) in several countries of central and eastern Europe. Voivodeships have existed since medieval times and the area of extent of voivodeship resembles that of a duchy in western medieval ...
. Passenger trains are mostly run using electrical multiple units (on electrified lines) or rail buses.
Buses
There is an extensive bus network that covers the entire city by three bus services, but no tram or subway exists. The three bus operators (KPKM, KPK and KZK) are owned by the city and each shares approximately a third of the lines and the bus fleet.Roads and highways
The National Roads ( pl, Droga krajowa) running through BiaŇāystok: * / :Budzisko
Budzisko is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Szypliszki, within SuwaŇāki County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Lithuania. It lies approximately north of Szypliszki, north-east of SuwaŇ ...
(Lithuania‚ÄďPoland border
The Lithuania‚ÄďPoland border is the state border between the Republic of Lithuania and the Republic of Poland. The length of the border is .. Page gives Polish PWN Encyklopedia as reference. It runs from the Lithuania‚ÄďPoland‚ÄďRussia tripo ...
) ‚Äď BiaŇāystok ‚Äď Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
‚Äď WrocŇāaw
WrocŇāaw (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
‚Äď Kudowa-Zdr√≥j
Kudowa-Zdr√≥j (german: Bad Kudowa, cz, Chudoba), or simply Kudowa, is a town located below the Table Mountains in KŇāodzko County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in the southwestern part of Poland. It has a population of around 10,000 and is locate ...
( Czech‚ÄďPolish border)
* : Rzeszów
Rzesz√≥w ( , ; la, Resovia; yi, ◊®◊ô◊ô◊©◊ź ''Raisha'')) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the WisŇāok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzesz√≥w has been the capital of the Subcarpathian Vo ...
‚Äď Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of t ...
‚Äď Bielsk Podlaski
Bielsk Podlaski ( be, –Ď–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Ā–ļ –ü–į–ī–Ľ—Ź—Ā–ļ—Ė, , yi, ◊Ď◊ô◊Ę◊ú◊°◊ß, Bielsk) is a town in eastern Poland, within Bielsk County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 24,883.
Geography
Bielsk Podla ...
‚Äď BiaŇāystok ‚Äď KuŇļnica (Belarus‚ÄďPoland border
The Belarusian-Polish border is the state border between the Republic of Poland (EU member) and the Republic of Belarus (Union State). It has a total length of , or
)
* : GoŇādap
GoŇādap ( or variant ''Goldapp''; lt, Geldupńó, Geldapńó, Galdapńó) is a town in northeastern Poland, in the region of Masuria, seat of GoŇādap County in the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship. It is located on the GoŇādapa River, between the Szeskie ...
(Poland‚ÄďRussia border
The modern Poland‚ÄďRussia border is a nearly straight-line division between the Republic of Poland (a European Union Member state of the European Union, member) and the Russian Federation (a Commonwealth of Independent States, CIS member) Enc ...
)-EŇāk
EŇāk (; former pl, ŇĀek; german: Lyck; Old Prussian: ''Luks''; lt, Lukas), also spelled Elk in English, is a small city in northeastern Poland with 61,677 inhabitants as of December 2021. It was assigned to Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship in 1999, ...
-BiaŇāystok-Bobrowniki
Bobrowniki (; german: Beberen) is a village in Lipno County, Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Bobrowniki. It lies approximately south-west of Lipno an ...
(Belarus‚ÄďPoland border
The Belarusian-Polish border is the state border between the Republic of Poland (EU member) and the Republic of Belarus (Union State). It has a total length of , or
)
The expressways
Expressway may refer to:
*Controlled-access highway, the highest-grade type of highway with access ramps, lane markings, etc., for high-speed traffic.
*Limited-access road, a lower grade of highway or arterial road.
*Expressway, the fictional slide ...
( pl, Droga ekspresowa) near BiaŇāystok:
* / : BiaŇāystok ‚Äď Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
‚Äď WrocŇāaw
WrocŇāaw (; german: Breslau, or . ; Silesian German: ''Brassel'') is a city in southwestern Poland and the largest city in the historical region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the River Oder in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Europe, rou ...
* ''(projected)'': Rzeszów
Rzesz√≥w ( , ; la, Resovia; yi, ◊®◊ô◊ô◊©◊ź ''Raisha'')) is the largest city in southeastern Poland. It is located on both sides of the WisŇāok River in the heartland of the Sandomierz Basin. Rzesz√≥w has been the capital of the Subcarpathian Vo ...
‚Äď Lublin
Lublin is the ninth-largest city in Poland and the second-largest city of historical Lesser Poland. It is the capital and the center of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 336,339 (December 2021). Lublin is the largest Polish city east of t ...
‚Äď Bielsk Podlaski
Bielsk Podlaski ( be, –Ď–Ķ–Ľ—Ć—Ā–ļ –ü–į–ī–Ľ—Ź—Ā–ļ—Ė, , yi, ◊Ď◊ô◊Ę◊ú◊°◊ß, Bielsk) is a town in eastern Poland, within Bielsk County in the Podlaskie Voivodeship. As of December 2021, the town has a population of 24,883.
Geography
Bielsk Podla ...
‚Äď BiaŇāystok ‚Äď KuŇļnica (Belarus‚ÄďPolish border)
The Voivodeship road
According to classes and categories of public roads in Poland, a voivodeship road ( pl, droga wojewódzka) is a category of roads one step below national roads in importance. The roads are numbered from 100 to 993. Total length of voivodeship r ...
s ( pl, Droga wojew√≥dzka) running through BiaŇāystok::
* : Trasa NiepodlegŇāoŇõci (Narodowych SiŇā Zbrojnych Street, NiepodlegŇāoŇõci Avenue, Padarewskiego Avenue)
* : TysińÖclecia PaŇĄstwa Polskiego Avenue ( pl, aleja TysińÖclecia PaŇĄstwa Polskiego)
* : PorosŇāy - BiaŇāystok - SupraŇõl - Krynki
* : BiaŇāystok - Wysokie Mazowieckie
Wysokie Mazowieckie is a town in north-eastern Poland, in Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the capital of Wysokie Mazowieckie County. Population is 10,034 .
In town there is one of the biggest dairy companies in this part of Europe - " Mlekovita ...
In BiaŇāystok Country ( pl, powiat biaŇāostocki) there are also Poviat roads ( pl, Droga powiatowa) which connect BiaŇāystok with other towns in the area:
Bicycle
By 2020, there were already over 158 km of bicycle paths in Bialystok. The municipal bicycle renting system is called BiKeR and was opened in 2014. The system initially based on 30 stations equipped with 300 bikes. The city has four public bicycle repair stations, in which one can fix their private bikes. The stations are located in places where the highest traffic of city bikes was observed.Airports
A civil airport, BiaŇāystok-Krywlany Airport, lies within the city limits, but does not provide regularly scheduled service, being currently the largest city in the European Union without an operating commercial airport. There were plans in 2011 to build a new regional airport, ''BiaŇāystok-Saniki Airport'', that would have provided flights within Europe.Education
 Higher education in the city can be traced back to the second half of the eighteenth century when the ownership of the city was inherited by
Higher education in the city can be traced back to the second half of the eighteenth century when the ownership of the city was inherited by Field Crown Hetman
Field may refer to:
Expanses of open ground
* Field (agriculture), an area of land used for agricultural purposes
* Airfield, an aerodrome that lacks the infrastructure of an airport
* Battlefield
* Lawn, an area of mowed grass
* Meadow, a grass ...
Jan Klemens Branicki
Count Jan Klemens Branicki (also known as Jan Kazimierz Branicki; 21 September 1689 ‚Äď 9 October 1771) was a Polish nobleman, magnate and Hetman, Field Crown Hetman of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth between 1735 and 1752, and Great Crown ...
. As a patron of the arts and sciences, Branicki encouraged numerous artists and scientists to settle in BiaŇāystok to take advantage of Branicki's patronage. In 1745 Branicki established Poland's first military college, the School of Civil and Military Engineering, in the city.
Since the fall of communism many privately funded institutions of higher educations have been founded and their number is still increasing. Currently BiaŇāystok is home to one principal public university
A public university or public college is a university or college that is in owned by the state or receives significant public funds through a national or subnational government, as opposed to a private university. Whether a national universit ...
(University of BiaŇāystok
The University of Bialystok is the largest university in the north-eastern region of Poland, educating in various fields of study, including humanities, social and natural sciences and mathematics. It has nine faculties, including a foreign one ...
) and two other public specialist universities (BiaŇāystok Technical University and Medical University of BiaŇāystok
The Medical University of BiaŇāystok (UMB; Polish: ''Uniwersytet Medyczny w BiaŇāymstoku'') is a medical university located in BiaŇāystok, the capital of Podlaskie Voivodeship in northeastern Poland.
The university is home to the Medical Depart ...
). Some institutions, such as Musical Academy in BiaŇāystok, are branches of their parent institutions in other cities, usually in Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officia ...
.
Notable residents
 Over the centuries, a number of people from BiaŇāystok have been prominent in the fields of science, language, politics, religion, sports, visual arts and performing arts. This environment was created in the mid-eighteenth century by the patronage of
Over the centuries, a number of people from BiaŇāystok have been prominent in the fields of science, language, politics, religion, sports, visual arts and performing arts. This environment was created in the mid-eighteenth century by the patronage of Jan Klemens Branicki
Count Jan Klemens Branicki (also known as Jan Kazimierz Branicki; 21 September 1689 ‚Äď 9 October 1771) was a Polish nobleman, magnate and Hetman, Field Crown Hetman of the Polish‚ÄďLithuanian Commonwealth between 1735 and 1752, and Great Crown ...
for the arts and sciences. These include Ryszard Kaczorowski
Ryszard Kaczorowski, GCMG (; 26 November 1919 ‚Äď 10 April 2010) was a Polish statesman. From 1989 to 1990, he served as the last President of Poland- in-exile. He succeeded Kazimierz Sabbat, and resigned his post following Poland's regaini ...
, last émigré
An ''émigré'' () is a person who has emigrated, often with a connotation of political or social self-exile. The word is the past participle of the French ''émigrer'', "to emigrate".
French Huguenots
Many French Huguenots fled France followi ...
President of the Republic of Poland
The president of Poland ( pl, Prezydent RP), officially the president of the Republic of Poland ( pl, Prezydent Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej), is the head of state of Poland. Their rights and obligations are determined in the Constitution of Polan ...
, L. L. Zamenhof
L. L. Zamenhof (15 December 185914 April 1917) was an ophthalmologist who lived for most of his life in Warsaw. He is best known as the creator of Esperanto, the most widely used constructed international auxiliary language.
Zamenhof first dev ...
, the creator of Esperanto, Albert Sabin
Albert Bruce Sabin ( ; August 26, 1906 ‚Äď March 3, 1993) was a Polish-American medical researcher, best known for developing the oral polio vaccine, which has played a key role in nearly eradicating the disease. In 1969‚Äď72, he served as the ...
, co-developer of the polio vaccine
Polio vaccines are vaccines used to prevent poliomyelitis (polio). Two types are used: an inactivated poliovirus given by injection (IPV) and a weakened poliovirus given by mouth (OPV). The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends all chil ...
, Izabella Scorupco
Izabella Scorupco (born Izabela Dorota Skorupko; 4 June 1970) is a Polish-born Swedish actress, singer and model. She is best known for having played Bond girl Natalya Simonova in the 1995 James Bond film ''GoldenEye''. She is also known for her ...
, actress, Max Weber
Maximilian Karl Emil Weber (; ; 21 April 186414 June 1920) was a German sociologist, historian, jurist and political economist, who is regarded as among the most important theorists of the development of modern Western society. His ideas profo ...
, painter. Tomasz BagiŇĄski
Tomasz "Tomek" BagiŇĄski (, born 10 January 1976 in BiaŇāystok) is a Polish illustrator, animator, producer and director. He is a self-taught artist.
Education
BagiŇĄski studied architecture at the Warsaw University of Technology. Works
His firs ...
illustrator, animator and director Oscar
Oscar, OSCAR, or The Oscar may refer to:
People
* Oscar (given name), an Irish- and English-language name also used in other languages; the article includes the names Oskar, Oskari, Oszk√°r, √ďscar, and other forms.
* Oscar (Irish mythology), ...
nominee in 2002 for '' The Cathedral''.
References
Notes
Further reading
* ŇĀukasz KaŇļmierczakTrzy procent odmiennoŇõci
(Three percent of different) ‚Äď article describing results of Polish census 2002 and minorities in Poland, citing census data * Janusz ŇĽarnowski, ''"SpoŇāeczeŇĄstwo Drugiej Rzeczypospolitej 1918‚Äď1939"'', Warszawa 1973 * Eugeniusz Mironowicz, ''"BiaŇāoruŇõ"'', Trio, Warszawa, 1999, * Yvette Walczak, ''"Let Her Go!"'', Naomi Roth Publishing, London, 2012,
External links
*Osiedla.BiaŇāystok.pl
VisitBiaŇāystok.com
*
Official Site BiaŇāystok City Transport
Google Transit in BiaŇāystok
*
BiaŇāystok
at the B&F Compendium of Jewish Genealogy {{DEFAULTSORT:Bialystok Cities and towns in Podlaskie Voivodeship City counties of Poland Cities with powiat rights Podlachian Voivodeship Belostoksky Uyezd BiaŇāystok Voivodeship (1919‚Äď1939) Belastok Region Holocaust locations in Poland Jewish communities destroyed in the Holocaust